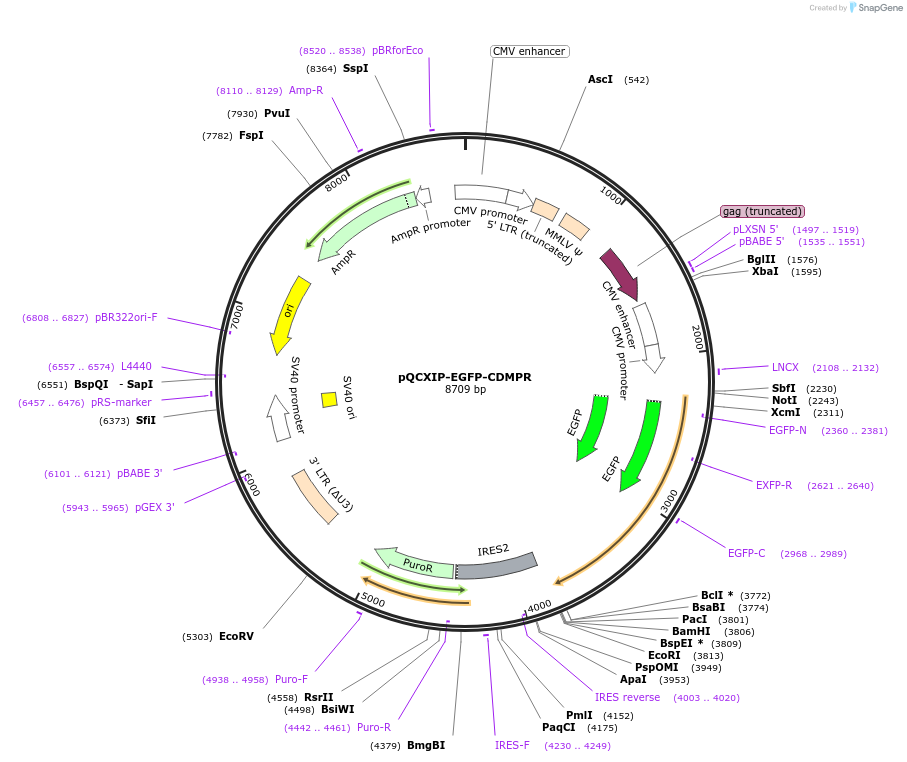
pQCXIP-EGFP-CDMPR
(Plasmid
#182642)
-
PurposeMammalian expression vector encoding a protein fusion composed of an N-terminal ER targeting sequence of hemagglutinin (HA), followed by EGFP and murine CDMPR (without its signal peptide)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 182642 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepQCXIP
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech/Takara Bio
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 7181
- Total vector size (bp) 8709
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Retroviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCDMPR
-
Alt nameCDMPR46
-
Alt nameCation-dependent mannose-6-phosphate receptor
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse), Synthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)1557
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- N-terminal ER targeting sequence of hemagglutinin (HA) (N terminal on insert)
- EGFP (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site PacI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer ACGCCATCCACGCTGTTTTGACCT
- 3′ sequencing primer AAGCGGCTTCGGCCAGTAACGTTA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pQCXIP-EGFP-CDMPR was a gift from Martin Spiess (Addgene plasmid # 182642 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:182642 ; RRID:Addgene_182642) -
For your References section:
Retrograde transport of CDMPR depends on several machineries as analyzed by sulfatable nanobodies. Buser DP, Bader G, Spiess M. Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Mar 21;5(7). pii: 5/7/e202101269. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101269. Print 2022 Mar. 10.26508/lsa.202101269 PubMed 35314489