-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 18119 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
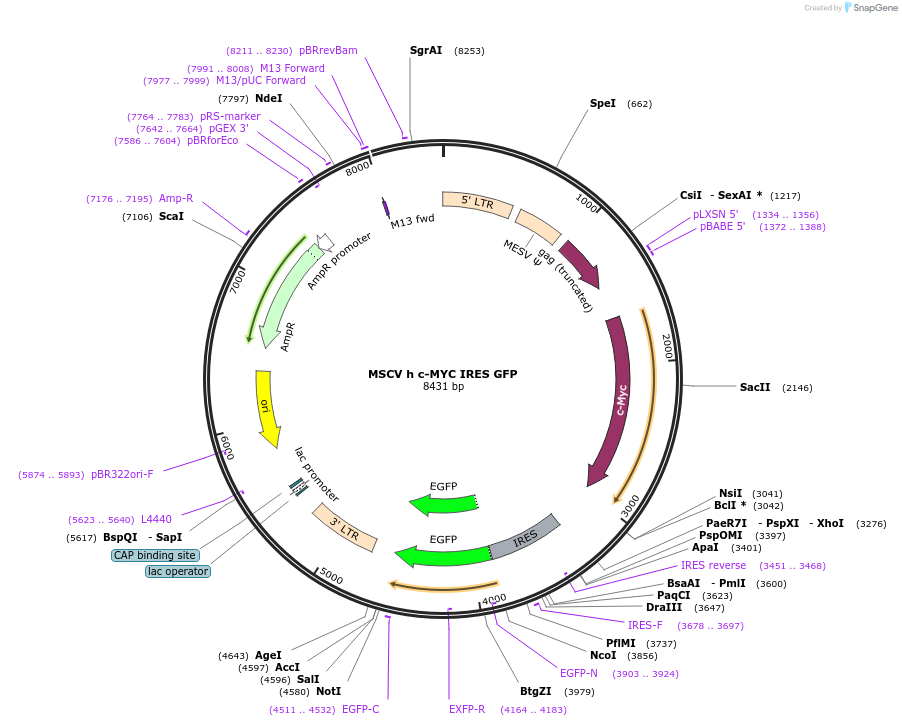
Vector backboneMSCV IRES GFP
-
Backbone manufacturerDr. Robert Hawley of George Washington University
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5660
-
Vector typeRetroviral
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namec-MYC
-
Alt namepMIG-cMYC
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1858
-
MutationThe CUG which is the start site for Myc I is present, however, there is a 3bp deletion between this and the ATG start site for Myc II.
-
GenBank IDNM_002467
-
Entrez GeneMYC (a.k.a. MRTL, MYCC, bHLHe39, c-Myc)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- GFP (C terminal on backbone)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Addgene Notes
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byThe MSCV plasmid is owned and was provided by Dr. Robert Hawley of George Washington University. The IRES-GFP DNA was developed by Dr. Arthur Nienhuis of St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (SJCRH). Dr. John L. Cleveland cloned the human c-myc gene into the construct while at SJCRH. Dr. Cleveland obtained an MTA for this construct from SJCRH when he moved to the Scripps Research Institute, Florida.
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The MSCV vector is described in; Hawley, R.G., Lieu, F.H.L., Fong, A.Z.C., and Hawley, T.S. Versatile retroviral vectors for potential use in gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1: 136-138, 1994.
Use of the construct is described in; Park, I., Zhao, R., West, J.A., Yabuuchi, A., Huo, H., Ince, T.A., Lerou, P.H., Lensch, M.W., and Daley, G.Q. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature, 451, 141-146, 2008.
Please note that the assembled sequence presented here is not 100% reflective of the actual sequence. See the Addgene diagnostic digest (found under the Resource Information section of the plasmid page) for additional information on the expected plasmid size. Addgene has found another HindIII site at the end of the MYC gene (see our quality control sequence).
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
MSCV h c-MYC IRES GFP was a gift from John Cleveland (Addgene plasmid # 18119 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:18119 ; RRID:Addgene_18119)