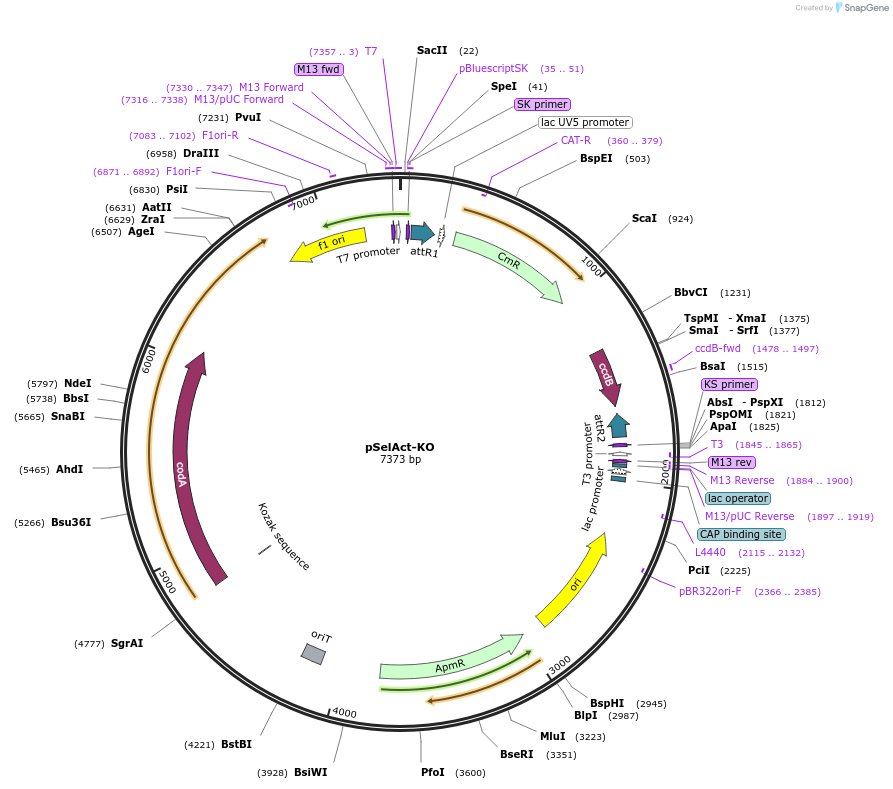
pSelAct-KO
(Plasmid
#174374)
-
Purpose(Empty Backbone) Plasmid for unmarked deletions, pUC19 backbone, Apr resistant casette, codA::app counterselection casette, gateway compatible
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 174374 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepUC19
- Backbone size (bp) 7373
-
Modifications to backboneApmR resistance cassette for integration, codA:upp cassette for counterselection, Gateway C1 cassette to clone in flanking homologous regions
-
Vector typeVector for 2-step knockout by homologous recombination
- Promoter N/A
-
Selectable markerscodA:upp counterselection
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Apramycin, 25 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)ccdB Survival
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gateway Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer GCATTAGGCACCCCAGGCTTTA
- 3′ sequencing primer TGCAGACTGGCTGTGTATAAGG
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byJeff Chang, Oregon State University
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Also known as pSelAct. For cloning in homology arms, can use Gateway, restriction-ligation, or homology-based cloning such as Gibson/Infusion cloning. Please cite at minimum paper 1) and a secondary paper that is most appropriate to your system of interest (2 or 3).
1. First development of pSelAct for knockouts in Rhodococcus equi:
Geize, R. van der, Jong, W. de, Hessels, G. I., Grommen, A. W. F., Jacobs, A. A. C., and Dijkhuizen, L. 2008. A novel method to generate unmarked gene deletions in the intracellular pathogen Rhodococcus equi using 5-fluorocytosine conditional lethality. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:e151
2. First development of pSelAct with Gateway cassette for knockouts in Rhodococcus fasicans:
Savory, E. A., Weisberg, A. J., Stevens, D. M., Creason, A. L., Fuller, S. L., Pearce, E. M., and Chang, J. H. 2020. Phytopathogenic Rhodococcus Have Diverse Plasmids With Few Conserved Virulence Functions. Front Microbiol. 11:1022
3. Later referred to as pSelAct-KO after optimization for knockouts in Clavibacter:
Stevens, D. M., Tang, A., and Coaker, G. 2021. A Genetic Toolkit for Investigating Clavibacter Species: Markerless Deletion, Permissive Site Identification, and an Integrative Plasmid. Mol Plant-microbe Interactions. 34:1336–1345
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pSelAct-KO was a gift from Gitta Coaker (Addgene plasmid # 174374 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:174374 ; RRID:Addgene_174374) -
For your References section:
A Genetic Toolkit for Investigating Clavibacter Species: Markerless Deletion, Permissive Site Identification, and an Integrative Plasmid. Stevens DM, Tang A, Coaker G. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021 Dec;34(12):1336-1345. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-07-21-0171-TA. Epub 2021 Dec 10. 10.1094/MPMI-07-21-0171-TA PubMed 34890250