-
PurposeUsed to generate stable mRNA for heterologous expression experiments (includes polyA tail)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 174006 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
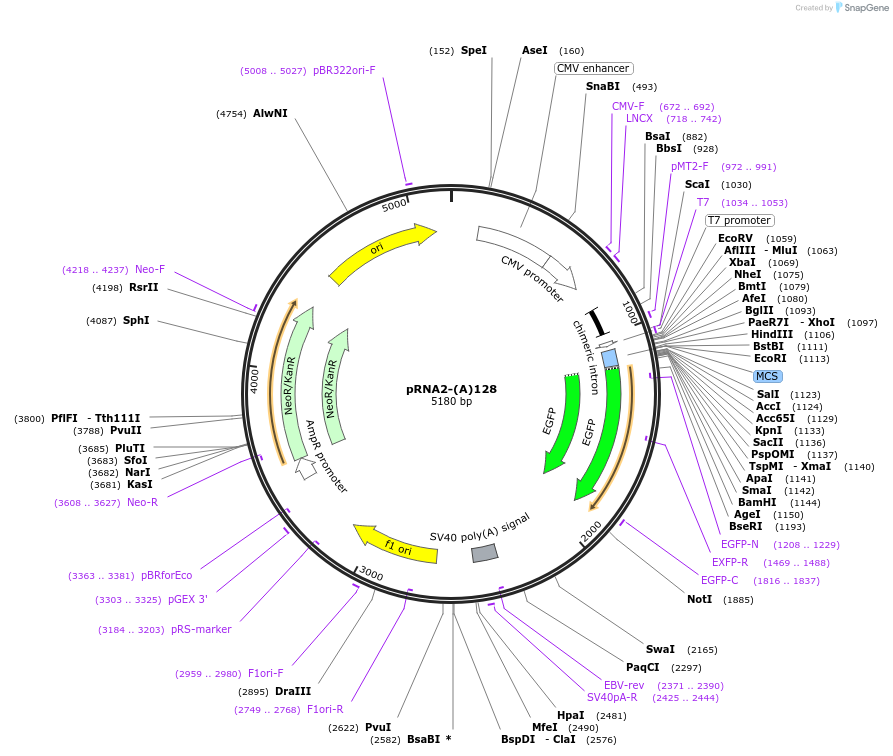
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCI
-
Backbone manufacturerPromega
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4000
- Total vector size (bp) 5180
-
Modifications to backboneT7 promoter optimized and multiple cloning sequence heavily modified. Two copies of the human beta-globin 3'UTR were added. A 128bp polyA tail was added with downstream restriction enzyme cut sites. Ampicillin resistance gene was replaced with Kanamycin.
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameeGFP
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)720
-
GenBank IDCloned from U55762.1
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMVfor
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Addgene Notes
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pRNA2-(A)128 was a gift from Stephen Ikeda (Addgene plasmid # 174006) -
For your References section:
A Simple, Highly Efficient Method for Heterologous Expression in Mammalian Primary Neurons Using Cationic Lipid-mediated mRNA Transfection. Williams DJ, Puhl HL, Ikeda SR. Front Neurosci. 2010 Nov 4;4:181. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2010.00181. eCollection 2010. 10.3389/fnins.2010.00181 PubMed 21267423