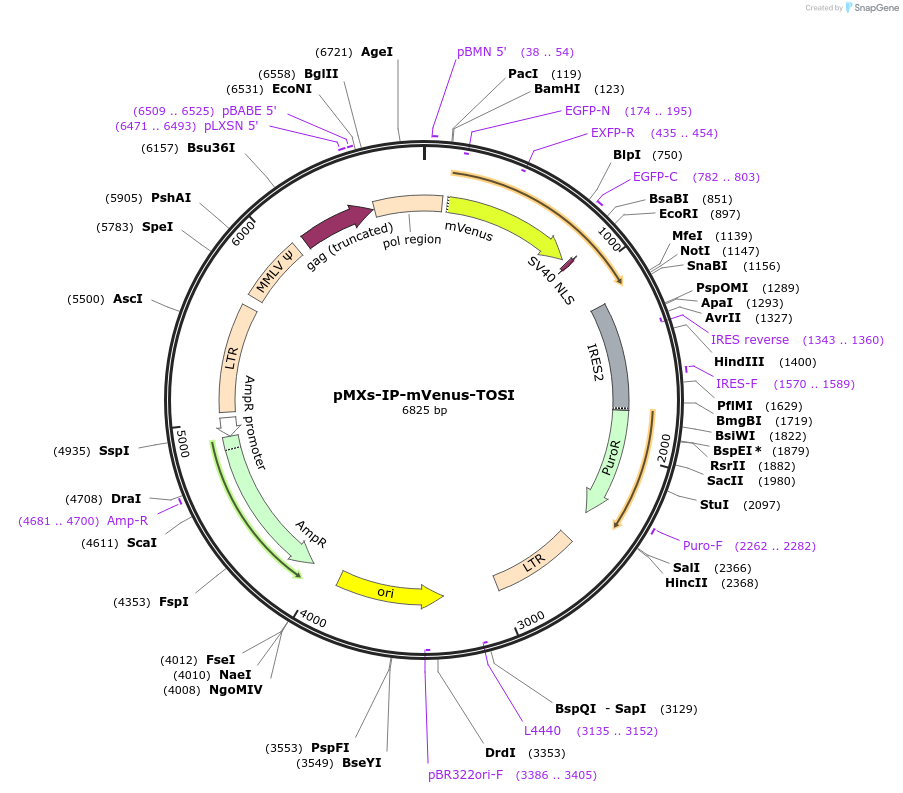
-
PurposemVenus-TOSI (TOr-Signal-Indicator) is a fluorescent reporter for mTORC1 signaling (monitoring PDCD4 degradation) which can be introduced to mammalian cells by retrovirus vector.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 172491 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepMXs-IP
-
Backbone manufacturerToshi Kitamura at University of Tokyo
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5800
- Total vector size (bp) 6800
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Retroviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namePdcd4
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)240
-
Entrez GenePdcd4 (a.k.a. D19Ucl, D19Ucla1, MA-, Ma3, T, Tis)
- Promoter MLV LTR
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- mVenus (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method TOPO Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer CCACCGCCCTCAAAGTAGACG
- 3′ sequencing primer NA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pMXs-IP-mVenus-TOSI was a gift from David Scadden (Addgene plasmid # 172491 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:172491 ; RRID:Addgene_172491) -
For your References section:
Imaging dynamic mTORC1 pathway activity in vivo reveals marked shifts that support time-specific inhibitor therapy in AML. Oki T, Mercier F, Kato H, Jung Y, McDonald TO, Spencer JA, Mazzola MC, van Gastel N, Lin CP, Michor F, Kitamura T, Scadden DT. Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 11;12(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20491-8. 10.1038/s41467-020-20491-8 PubMed 33431855