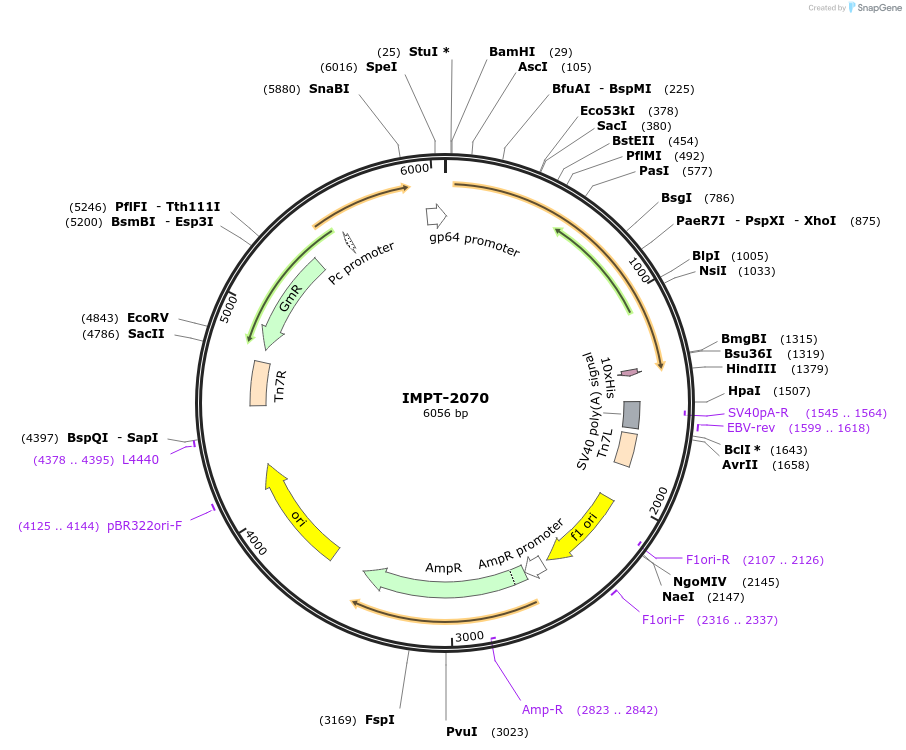
IMPT-2070
(Plasmid
#172092)
-
PurposepFastBac1 vector with GP64 promoter replacing polH promoter expressing A2aAR+BRIL GPCR
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 172092 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepFastBac1
-
Backbone manufacturerThermoFisher
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4731
- Total vector size (bp) 4800
-
Modifications to backbonegp64 promoter has replaced polyhedrin promoter
-
Vector typeInsect Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameHomo sapiens adenosine A2a receptor (ADORA2A)
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1344
-
GenBank IDNM_001278499.2
-
Entrez GeneADORA2A (a.k.a. A2aR, ADORA2, RDC8)
- Promoter gp64
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- cytochrome b562RIL
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CTA ACA ACG TGC CTT GTG TCA CGT
- 3′ sequencing primer CAAATGTGGTATGGCTGATT (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
IMPT-2070 was a gift from Raymond Stevens (Addgene plasmid # 172092 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:172092 ; RRID:Addgene_172092) -
For your References section:
Structural basis for allosteric regulation of GPCRs by sodium ions. Liu W, Chun E, Thompson AA, Chubukov P, Xu F, Katritch V, Han GW, Roth CB, Heitman LH, IJzerman AP, Cherezov V, Stevens RC. Science. 2012 Jul 13;337(6091):232-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1219218. 10.1126/science.1219218 PubMed 22798613