-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 16655 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
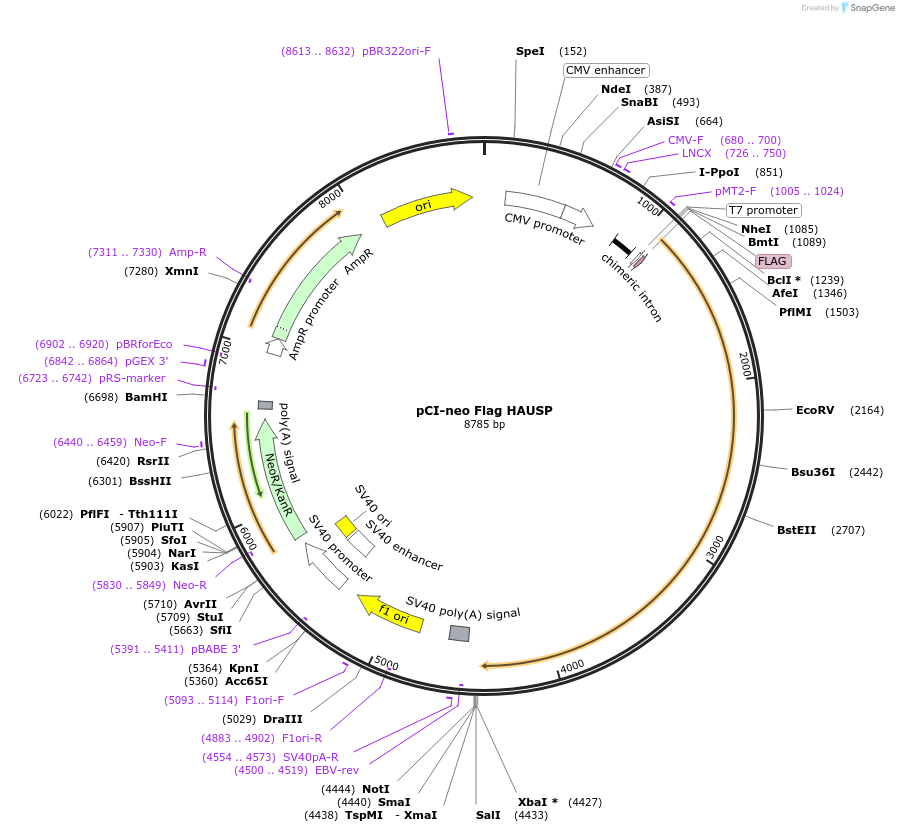
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCI-Neo
-
Backbone manufacturerPromega
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5472
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameHAUSP
-
Alt nameUSP7
-
Alt nameubiquitin specific peptidase 7
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Entrez GeneUSP7 (a.k.a. C16DELp13.2, DEL16P13.2, HAFOUS, HAUSP, TEF1)
- Promoter CMV
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- Flag (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XbaI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-F
- 3′ sequencing primer EBV-rev
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
A fragment of human HAUSP cDNA including the entire ORF was cloned into pCI-neo at the NheI and XbaI sites. (Please note that the XbaI site is blocked by overlapping methylation). A sequence including the Flag tag was added to one of the primers so that the encoded protein contains a Flag tag at the N-terminus.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCI-neo Flag HAUSP was a gift from Bert Vogelstein (Addgene plasmid # 16655 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:16655 ; RRID:Addgene_16655) -
For your References section:
HAUSP is required for p53 destabilization. Cummins JM, Vogelstein B. Cell Cycle. 2004 Jun . 3(6):689-92. 10.4161/cc.3.6.924 PubMed 15118411