-
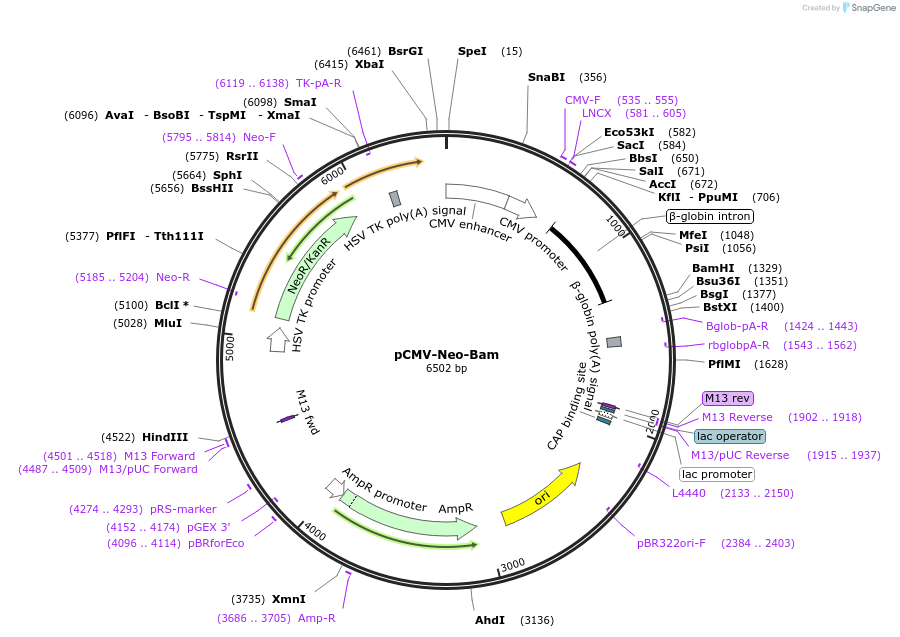
Purpose(Empty Backbone) Contains two independent transcription units--a CMV promoter/enhancer upstream of a MCS and a HSV thymidine kinase promoter/enhancer upstream of the neomycin resistance gene.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 16440 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCMV-Neo-Bam
-
Backbone manufacturerVogelstein Lab
- Backbone size (bp) 6600
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameNone
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer Bglob-intron-F
- 3′ sequencing primer Bglob-pA-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The vector pCMV-Neo-Bam was engineered to contain two independent transcription units. The first unit is comprised of a CMV promoter/enhancer upstream of a multiple cloning site, and splice and polyA sites to ensure appropriate processing. The second transcription unit includes a herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase promoter/enhancer upstream of the neomycin resistance gene.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCMV-Neo-Bam was a gift from Bert Vogelstein (Addgene plasmid # 16440 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:16440 ; RRID:Addgene_16440) -
For your References section:
Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Baker SJ, Markowitz S, Fearon ER, Willson JK, Vogelstein B. Science. 1990 Aug 24. 249(4971):912-5. 10.1126/science.2144057 PubMed 2144057