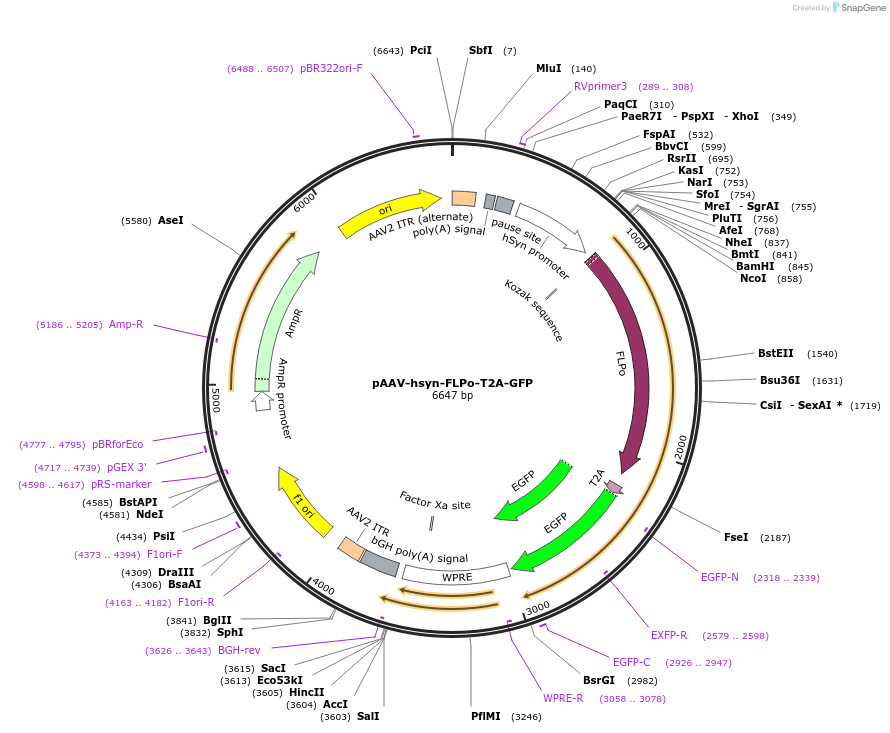
pAAV-hsyn-FLPo-T2A-GFP
(Plasmid
#161766)
-
Purposeexpress FLPo and GFP under the control of human synapsin promoter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 161766 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepAAV-hSynapsin
-
Backbone manufacturerAddgene
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4525
- Total vector size (bp) 6591
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert nameFLPo
-
SpeciesFLPo is a mouse codon-optimized FLP
- Promoter hSynapsin1
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 1
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer hSyn1pro-F
- 3′ sequencing primer WPRE-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert nameT2AEGFP
-
SpeciesAequorea victoria
- Promoter hSynapsin1
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 2
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer hSyn1pro-F
- 3′ sequencing primer WPRE-R
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made bypAAV-hSynapsin-Flpo addgene Plasmid #60663
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pAAV-hsyn-FLPo-T2A-GFP was a gift from Baoji Xu (Addgene plasmid # 161766 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:161766 ; RRID:Addgene_161766) -
For your References section:
TrkB-expressing paraventricular hypothalamic neurons suppress appetite through multiple neurocircuits. An JJ, Kinney CE, Tan JW, Liao GY, Kremer EJ, Xu B. Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 7;11(1):1729. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15537-w. 10.1038/s41467-020-15537-w PubMed 32265438