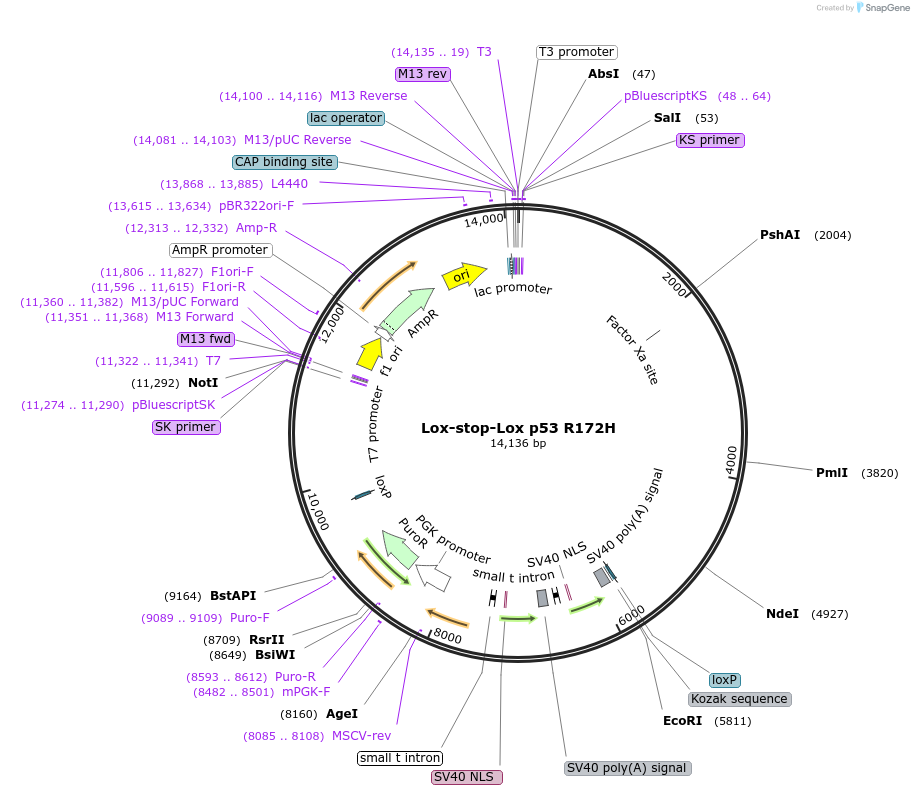
-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 14854 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBluescript
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3000
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Cre/Lox
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Stbl3
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namep53 R172H
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)17000
-
MutationStructural mutant R172H. (Murine p53 codon 172 corresponds to human codon 175).
-
Entrez GeneTrp53 (a.k.a. Tp53, bbl, bfy, bhy, p44, p53)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- Lox-STOP-lox (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ sequencing primer n/a
- 3′ sequencing primer T3
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Conditional mutant alleles of p53 were generated by introducing the LoxP-flanked transcriptional STOP cassette into intron 1 of the p53 gene. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to introduce an arg→his mutation at codon 172.
Note: This is a large plasmid that can undergo recombination. Bacterial colonies will grow slowly. If there are different colony sizes on a plate, the smaller ones are more likely to contain the correct plasmid.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
Lox-stop-Lox p53 R172H was a gift from Tyler Jacks (Addgene plasmid # 14854 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:14854 ; RRID:Addgene_14854) -
For your References section:
Mutant p53 gain of function in two mouse models of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Olive KP, Tuveson DA, Ruhe ZC, Yin B, Willis NA, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Jacks T. Cell. 2004 Dec 17. 119(6):847-60. 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.004 PubMed 15607980