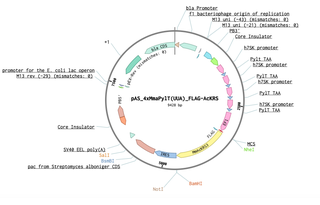
pAS_4xMma PylT(UUA)_FLAG-AcKRS
(Plasmid
#140010)
-
PurposePlasmid with 4xMmaP cassette and Mma PylRS for ochre (TAA) suppression; for transient or stable piggyBac-mediated integration
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 140010 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepAS
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameAcKRS-3
-
Alt name4xh7SK-Mma PylT (TAA) cassette
-
SpeciesMethanosarcina mazei
-
Insert Size (bp)1412
-
MutationL301M, L305I, Y306F, L309A, C348F
-
Entrez GenepylS (a.k.a. MSMAC_RS17105, MSMAC_3241)
- Promoter EF1
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- FLAG (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please note there are several ambiguous bases in the 2 small regions in the h7SK promoter and PylT TAA repeats in Addgene's NGS result. Depositor has confirmed plasmid is functional.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pAS_4xMma PylT(UUA)_FLAG-AcKRS was a gift from Simon Elsaesser (Addgene plasmid # 140010 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:140010 ; RRID:Addgene_140010) -
For your References section:
Methanomethylophilus alvus Mx1201 provides basis for mutual orthogonal pyrrolysyl tRNA/aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pairs in mammalian cells. Meineke B, Heimgartner J, Lafranchi L, Elsasser SJ. ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00571. 10.1021/acschembio.8b00571 PubMed 30260624