-
PurposeExpress TRACE editor together with a tdTomato reporter in pcDNA3.1(+) backbone
-
Depositing Lab
-
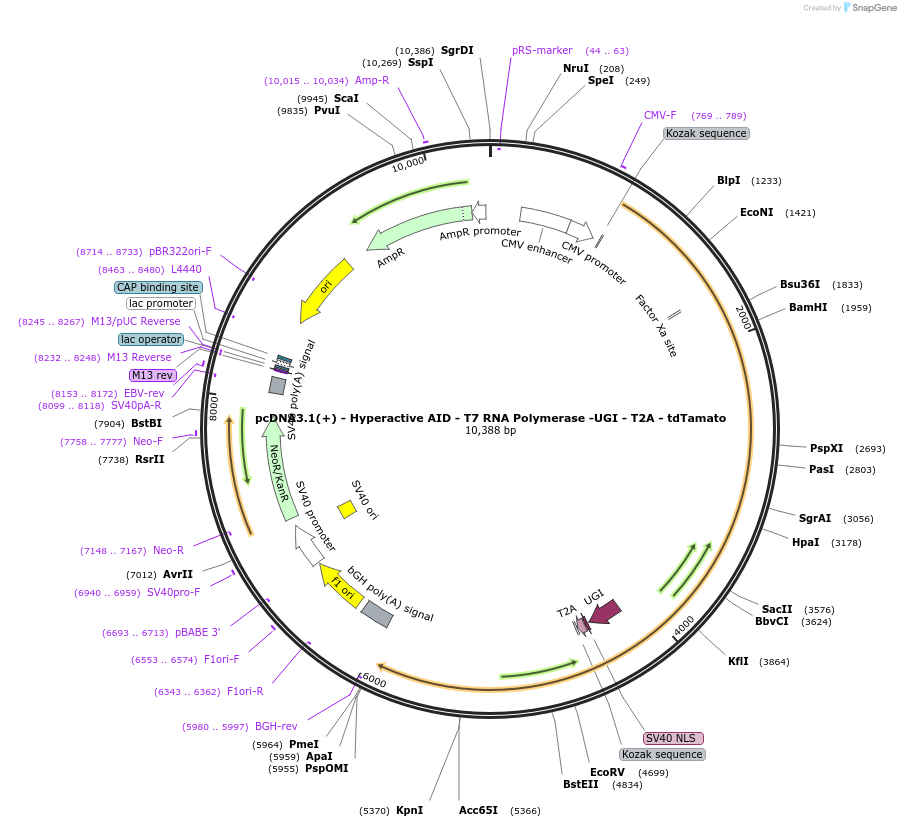
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 138610 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA3.1(+)
- Total vector size (bp) 10336
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert nameHyperactive AID
-
Alt namepcDNA3.1(+) - Hyperactive AID - T7 RNA Polymerase G645AQ744R-UGI - T2A - tdTomato
-
Insert Size (bp)585
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert nameT7 RNA Polymerase
-
Insert Size (bp)2646
Gene/Insert 3
-
Gene/Insert nametdTomato
-
Insert Size (bp)1428
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byHyperactive AID was cloned from pGH335_MS2-AID*Δ-Hygro obtained from Michael Bassik (Addgene plasmid # 85406)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pcDNA3.1(+) - Hyperactive AID - T7 RNA Polymerase -UGI - T2A - tdTamato was a gift from Fei Chen (Addgene plasmid # 138610 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:138610 ; RRID:Addgene_138610) -
For your References section:
Efficient, continuous mutagenesis in human cells using a pseudo-random DNA editor. Chen H, Liu S, Padula S, Lesman D, Griswold K, Lin A, Zhao T, Marshall JL, Chen F. Nat Biotechnol. 2019 Dec 16. pii: 10.1038/s41587-019-0331-8. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0331-8. 10.1038/s41587-019-0331-8 PubMed 31844291