-
PurposeMammalian expression of enhanced form of Flp recombinase fused to GFP
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 13788 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
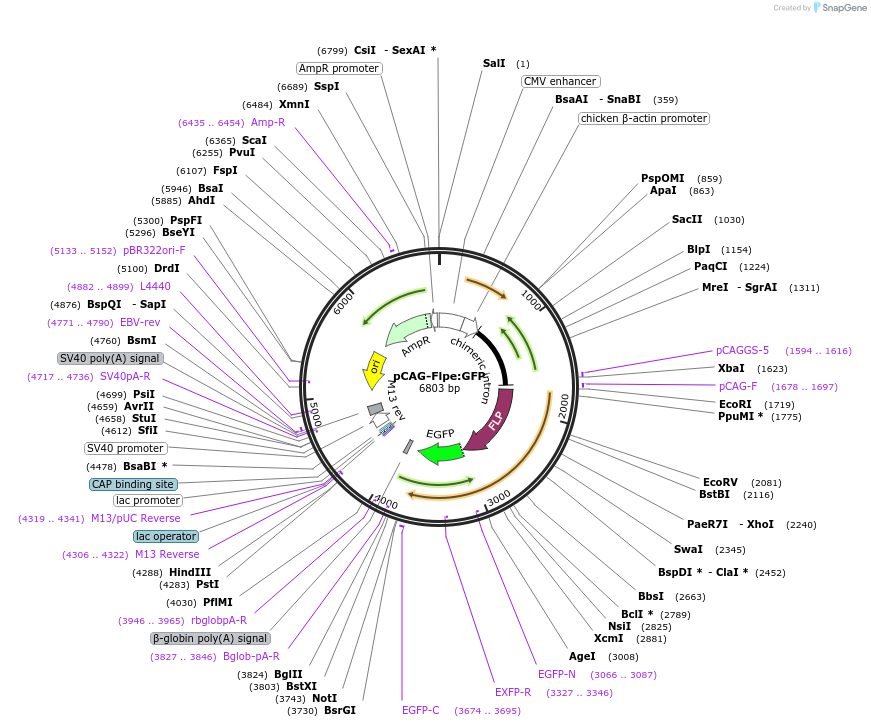
Vector backbonepCAGEN
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4779
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression ; Flp/FRT
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameFlpe-GFP fusion protein
-
SpeciesS. cerevisiae (budding yeast)
-
Insert Size (bp)2024
- Promoter CAG
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- GFP (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer pCAG-F
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byThe coding sequence of Flpe was amplified by PCR using pCMVscript-FlpeERT2 (Hunter et al. Genesis 41, 99-109 (2005)) obtained from Dr. S. Dymecki (Harvard Medical School) as a template. GFP was from pEGFP-N1 (Clontech).
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Kozak consensus sequence was added before the start ATG. Internal EcoRI site was destroyed by introducing a silent mutation.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCAG-Flpe:GFP was a gift from Connie Cepko (Addgene plasmid # 13788 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:13788 ; RRID:Addgene_13788) -
For your References section:
Controlled expression of transgenes introduced by in vivo electroporation. Matsuda T, Cepko CL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 16;104(3):1027-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610155104 10.1073/pnas.0610155104 PubMed 17209010