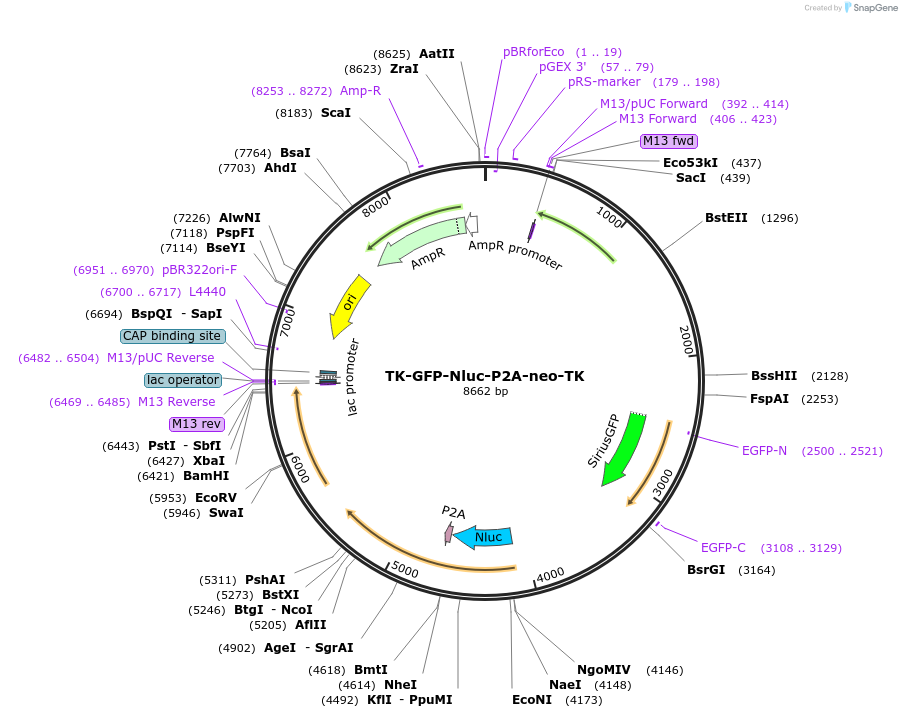
TK-GFP-Nluc-P2A-neo-TK
(Plasmid
#134896)
-
PurposeExpresses GFP protein and a fusion protein of Nluc-neo inserting into Cryptosporidium parvum TK locus
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 134896 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepUC19
-
Backbone manufacturerinvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 2300
- Total vector size (bp) 8663
-
Modifications to backboneNo
-
Vector typeCryptosporidium Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameTK-GFP-Nluc-P2A-Neo-TK
-
SpeciesCryptosporidium parvum
-
Insert Size (bp)5961
- Promoter Cryptosporidium actin and enolase
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SacI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site KpnI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GAGCTCCATTTGTCCTAACTTCA
- 3′ sequencing primer GGTACCCCTACCATAAGCATCA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
TK-GFP-Nluc-P2A-neo-TK was a gift from David Sibley (Addgene plasmid # 134896 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:134896 ; RRID:Addgene_134896) -
For your References section:
A Stem-Cell-Derived Platform Enables Complete Cryptosporidium Development In Vitro and Genetic Tractability. Wilke G, Funkhouser-Jones LJ, Wang Y, Ravindran S, Wang Q, Beatty WL, Baldridge MT, VanDussen KL, Shen B, Kuhlenschmidt MS, Kuhlenschmidt TB, Witola WH, Stappenbeck TS, Sibley LD. Cell Host Microbe. 2019 Jun 18. pii: S1931-3128(19)30252-5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.05.007. 10.1016/j.chom.2019.05.007 PubMed 31231046