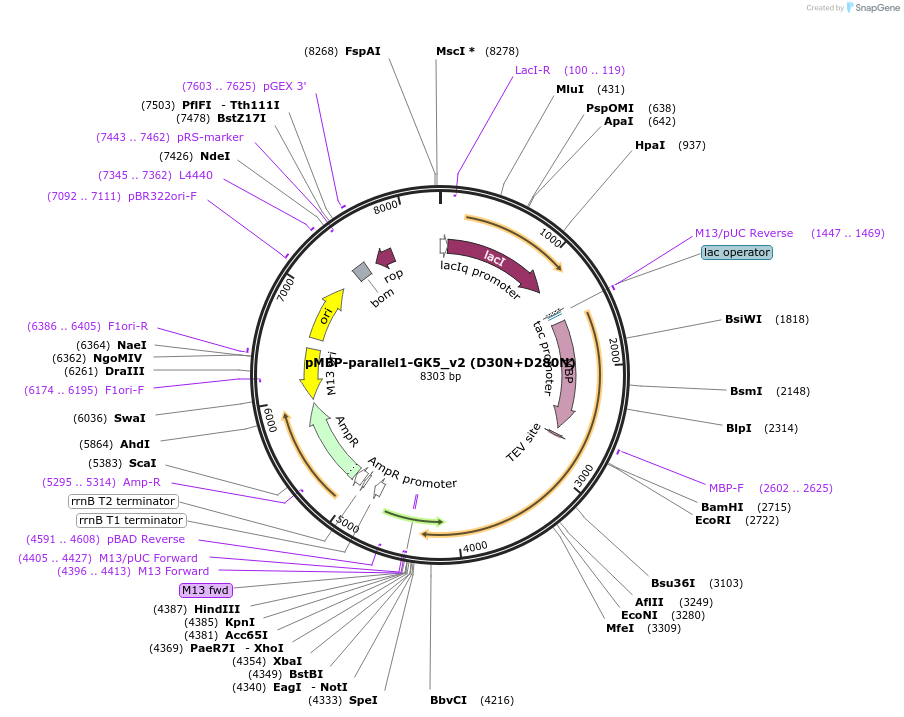
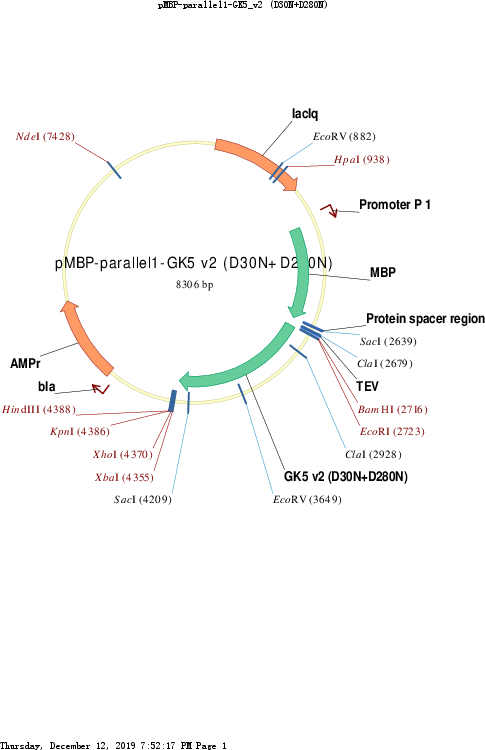
pMBP-parallel1-GK5_v2 (D30N+D280N)
(Plasmid
#134292)
-
PurposeExpresses GK5 (isoform 2)-D30N/D280N mutant in bacteria
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 134292 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepMBP-parallel1
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6700
- Total vector size (bp) 8300
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameGk5
-
Alt nameglycerol kinase 5 (putative)
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse)
-
Insert Size (bp)1605
-
Mutationchanged Aspartic Acids 30 and 280 to Asparagine
-
GenBank IDNM_001368879
-
Entrez GeneGk5 (a.k.a. AV095337, C330018K18Rik, G630067D24Rik)
- Promoter T7
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- MBP (N terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer GATGAAGCCCTGAAAGACGCGCAG
- 3′ sequencing primer TGCTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTGG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pMBP-parallel1-GK5_v2 (D30N+D280N) was a gift from Bruce Beutler (Addgene plasmid # 134292 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:134292 ; RRID:Addgene_134292) -
For your References section:
Skin-specific regulation of SREBP processing and lipid biosynthesis by glycerol kinase 5. Zhang D, Tomisato W, Su L, Sun L, Choi JH, Zhang Z, Wang KW, Zhan X, Choi M, Li X, Tang M, Castro-Perez JM, Hildebrand S, Murray AR, Moresco EMY, Beutler B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 27;114(26):E5197-E5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705312114. Epub 2017 Jun 12. 10.1073/pnas.1705312114 PubMed 28607088