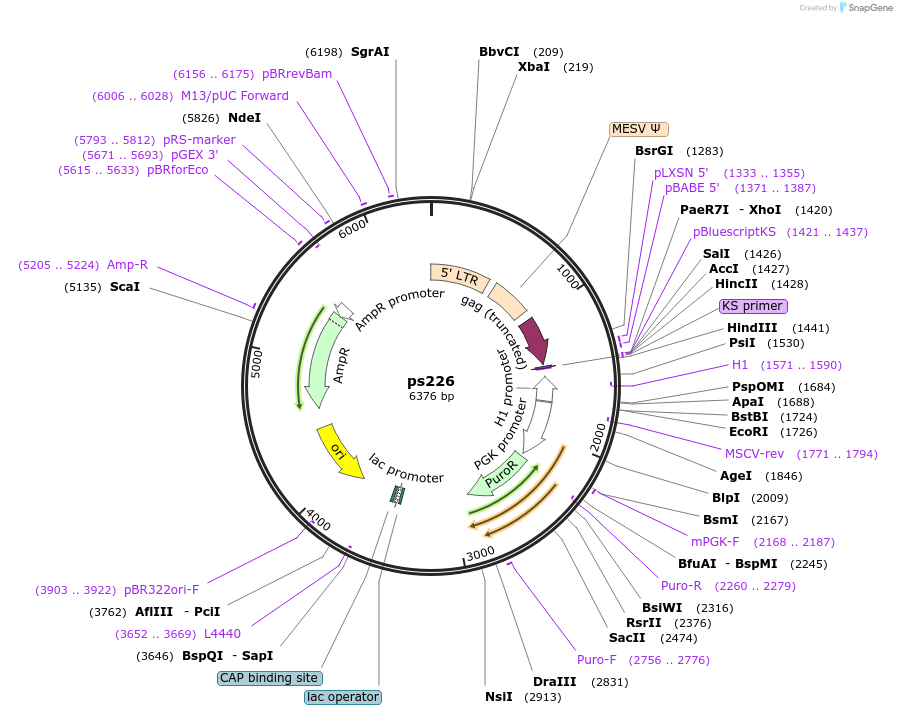
ps226
(Plasmid
#133557)
-
PurposeRNAi construct for knock-down of CDKN1A (Cip1, p21)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 133557 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepRETRO-SUPER
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6349
-
Vector typeRetroviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCDKN1A
-
gRNA/shRNA sequencegaccatgtggacctgtcac
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Entrez GeneCDKN1A (a.k.a. CAP20, CDKN1, CIP1, MDA-6, P21, SDI1, WAF1, p21CIP1)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site unknown (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site unknown (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer unknown
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
HMS clone ID number: HsSH00021241.
Ho Man Chan made the clone.
According to the clone donor, NOT identical to the shRNA reported in the paper (that is ps225) but this is a functional shRNA against ps226.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
ps226 was a gift from David Livingston (Addgene plasmid # 133557 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:133557 ; RRID:Addgene_133557) -
For your References section:
The p400 E1A-associated protein is a novel component of the p53 --> p21 senescence pathway. Chan HM, Narita M, Lowe SW, Livingston DM. Genes Dev. 2005 Jan 15;19(2):196-201. doi: 10.1101/gad.1280205. 10.1101/gad.1280205 PubMed 15655109