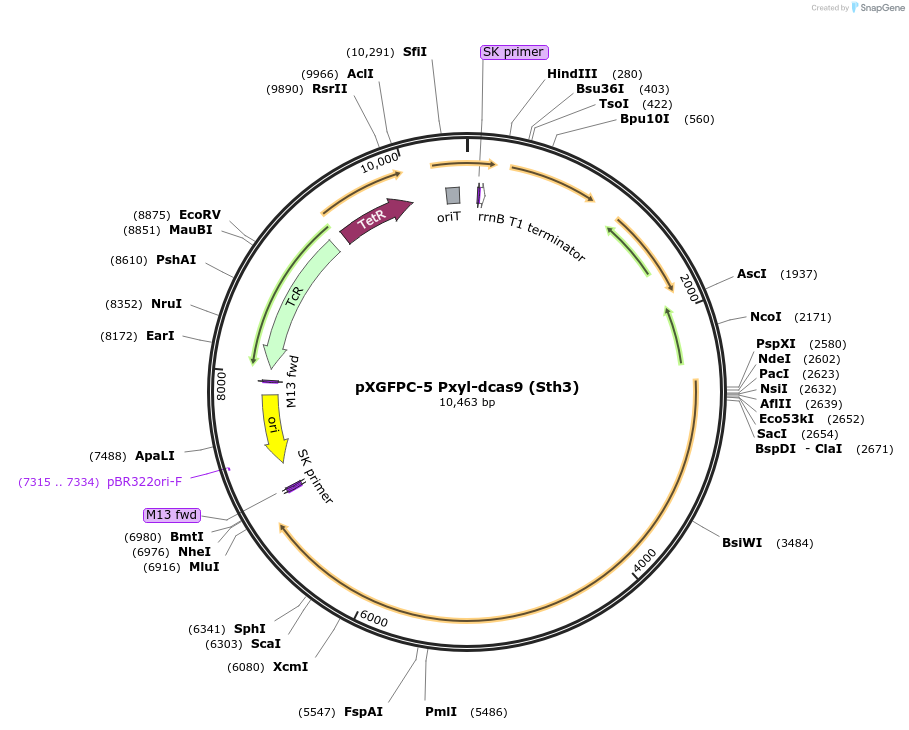
pXGFPC-5 Pxyl-dcas9 (Sth3)
(Plasmid
#133317)
-
Purposeexpresses dcas9 (Streptococcus thermophilus #3); repressed with 0.2% glucose, induced with 0.3% xylose; for homologous recombination at the xyl locus in Caulobacter crescentus; tetracycline resistance
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 133317 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepXGFPC-5
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 6296
- Total vector size (bp) 10463
-
Vector typeUnspecified
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Tetracycline, 10 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Top10
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namedcas9 (Streptococcus thermophilus #3)
-
SpeciesStreptococcus thermophilus
-
Insert Size (bp)4167
- Promoter xylose
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer TGGTCAGACAACCTACTTGCCGTC
- 3′ sequencing primer TCGGCTGCGGCGAGCGGTATCA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byJeremy M. Rock "Programmable transcriptional repression in mycobacteria using an orthogonal CRISPR interference platform" Nature microbiology 2017
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pXGFPC-5 Pxyl-dcas9 (Sth3) was a gift from Michael Laub (Addgene plasmid # 133317 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:133317 ; RRID:Addgene_133317) -
For your References section:
A CRISPR Interference System for Efficient and Rapid Gene Knockdown in Caulobacter crescentus. Guzzo M, Castro LK, Reisch CR, Guo MS, Laub MT. mBio. 2020 Jan 14;11(1):e02415-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02415-19. 10.1128/mBio.02415-19 PubMed 31937638