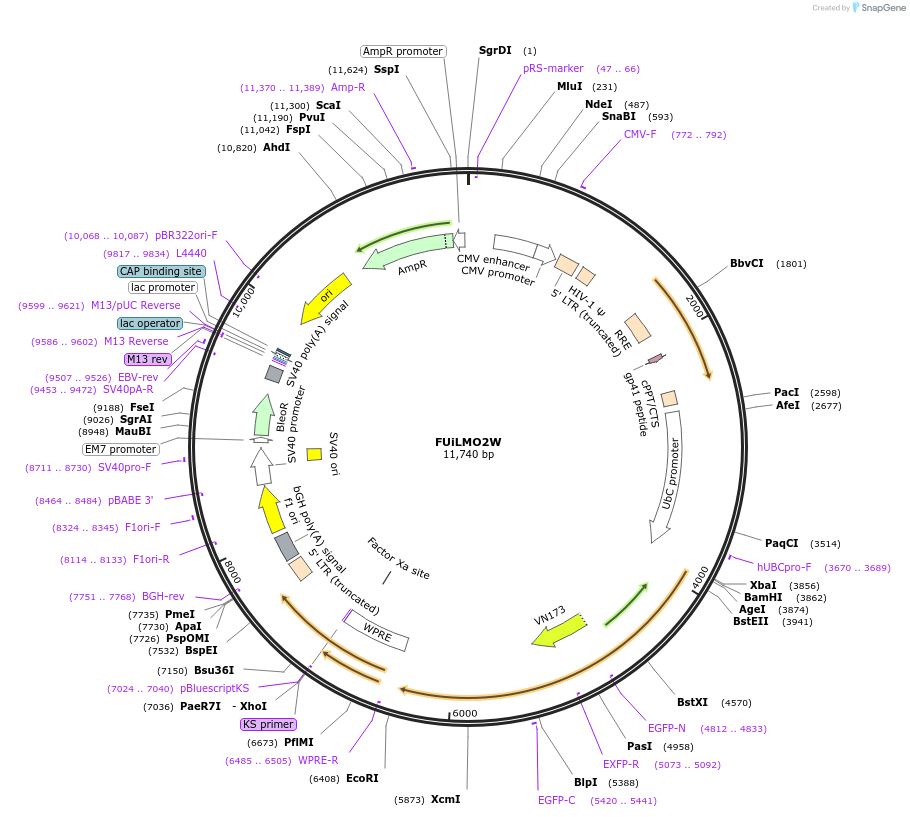
FUiLMO2W
(Plasmid
#129480)
-
Purpose3rd-generation lentiviral vector for iLMO2, an opto-chemogenetic probe for neuronal inhibition by light or chemical
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 129480 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backboneFUGW
-
Backbone manufacturerDavid Baltimore (Addgene plasmid # 14883)
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 9180
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Lentiviral
-
Selectable markersBleomycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameiLMO2
-
Alt nameinhibitory luminopsin 2
-
Alt nameeNpHR2.0-Nanolantern
-
SpeciesN. pharaonis, A. victoria, R. reniformis
-
Insert Size (bp)2526
- Promoter human ubiquitin C
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made bypAAV-CaMKIIa-eNpHR3.0-EYFP from Karl Deisseroth, Stanford U (Addgene #26971) and Nano-lantern/pcDNA3 from Takeharu Nagai, Osaka U (Addgene #51970)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
iLMO2 (NpHR-Nanolantern-ER export motif) from pcDNA3 vector was inserted using BamHI/EcoRI
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
FUiLMO2W was a gift from Robert Gross (Addgene plasmid # 129480 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:129480 ; RRID:Addgene_129480) -
For your References section:
Inhibitory luminopsins: genetically-encoded bioluminescent opsins for versatile, scalable, and hardware-independent optogenetic inhibition. Tung JK, Gutekunst CA, Gross RE. Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 24;5:14366. doi: 10.1038/srep14366. 10.1038/srep14366 PubMed 26399324