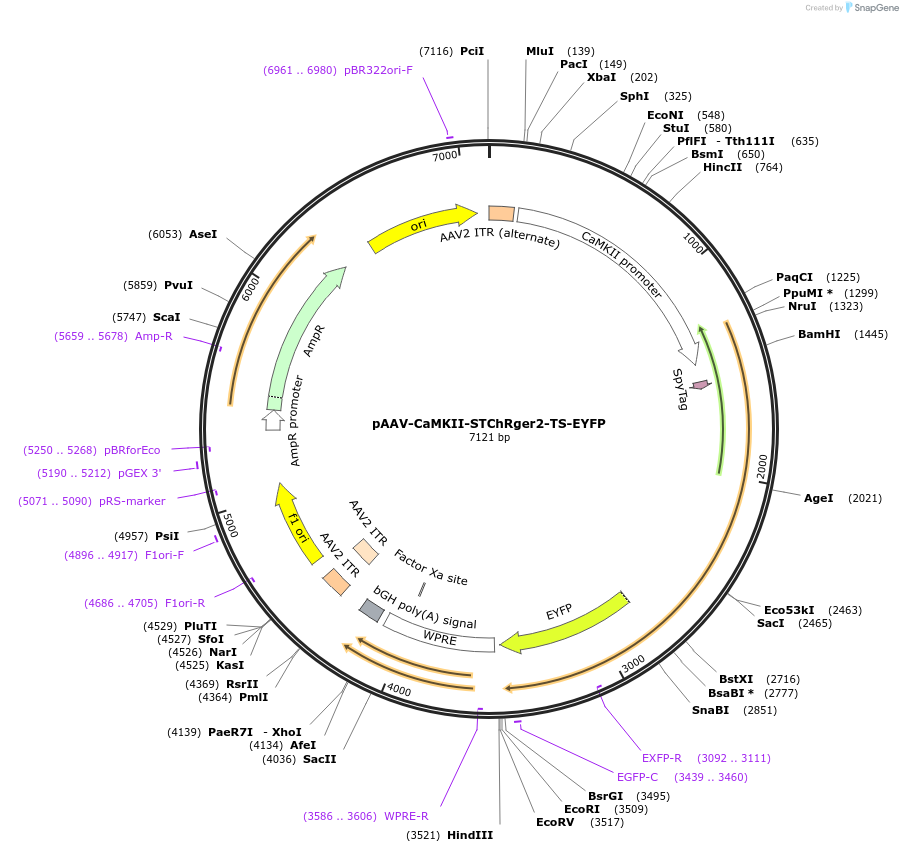
pAAV-CaMKII-STChRger2-TS-EYFP
(Plasmid
#129393)
-
PurposeSoma Targeted, High photocurrent, low-light sensitive channelrhodopsin (ChRger2) for optogenetic activation with systemic delivery or for low-light activation. Driven by the CamKIIa promoter.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 129393 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Want a viral vector made from this plasmid?
Make a packaging request and we'll get back to you.
Please log in to submit a packaging request.
-
SerotypeSelect serotype for details See details about
-
PricingSelect serotype and quantity $ USD for preparation of µL virus + $32 USD for plasmid.
-
How this works
- Place a request for a quantity of 2 (0.2 mL), 10 (1 mL), 25 (2.5 mL), or 50 (5 mL). Our all-inclusive pricing includes DNA production and QC.
- Addgene will quickly confirm that we can produce a high-quality prep for you.
- Track your request and place an order from within your account. Payment information must be added before we can begin processing your order.
- Receive your prep in 6–9 weeks after the MTA is approved by your organization.
- Learn more about our Packaged on Request Service.
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepAAV CaMKIIa WPRE pA
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5076
- Total vector size (bp) 7125
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namesoma targeted ChRger2
-
Alt nameSTChRger2
-
Insert Size (bp)2049
- Promoter CaMKIIa
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- Kv2.1-TS-EYFP (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer GcttcgttacGCCgagtgg
- 3′ sequencing primer CATAGCGTAAAAGGAGCAACA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Addgene NGS results detect a mixed population at base 2849 (T/G), which could result in a D21Y variant in EYFP. This construct fluoresces as expected.
Depositor has evidence that soma-targeted constructs may have different optical properties from their parent ChRgers and they have not been fully characterized. Users should be aware that they are beta-testing.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pAAV-CaMKII-STChRger2-TS-EYFP was a gift from Viviana Gradinaru (Addgene plasmid # 129393 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:129393 ; RRID:Addgene_129393) -
For your References section:
Machine learning-guided channelrhodopsin engineering enables minimally invasive optogenetics. Bedbrook CN, Yang KK, Robinson JE, Mackey ED, Gradinaru V, Arnold FH. Nat Methods. 2019 Oct 14. pii: 10.1038/s41592-019-0583-8. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0583-8. 10.1038/s41592-019-0583-8 PubMed 31611694