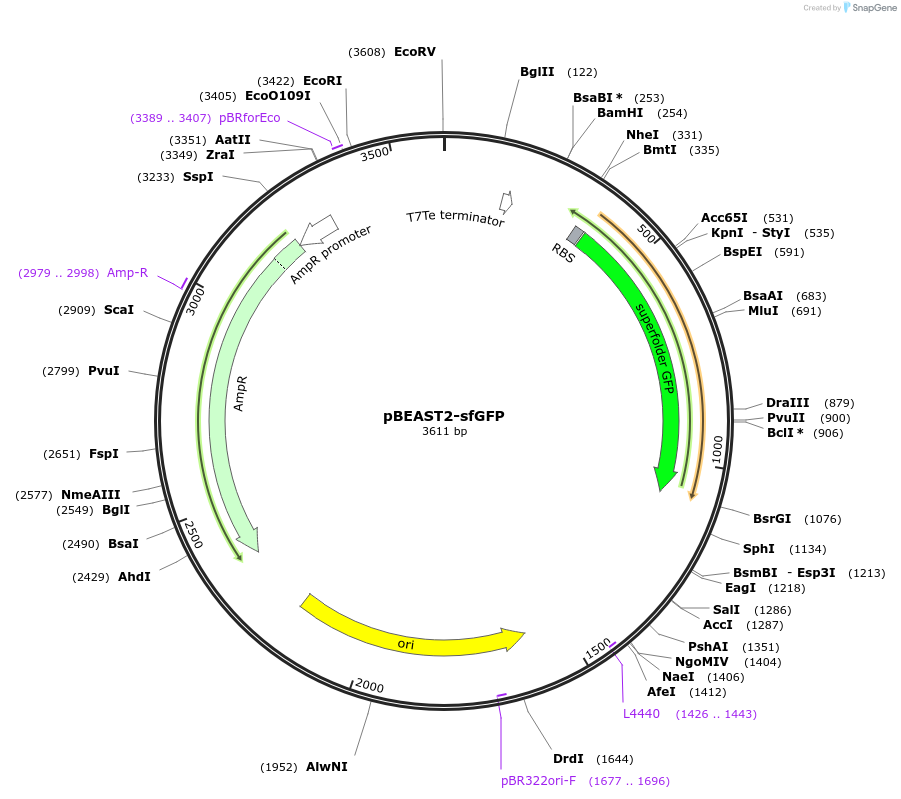
pBEAST2-sfGFP
(Plasmid
#126575)
-
PurposeStrong constitutive expression of super-folder GFP for cell-free expression
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 126575 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepBEST-OR2-OR1-Pr-UTR1-deGFP-T500
-
Modifications to backboneTwo 40bp spacers were added to the each end of the insert to facilitate Gibson assembly cloning into more complex constructs. Upstream and downstream terminators (B0014 and T500, respectively) were flanked by two 40bp spacers. The OR2-OR1-Pr promoter and UTR were conserved, but deGFP was replaced by sfGFP.
-
Vector typeSynthetic Biology ; Cell-Free Protein Synthesis
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)KL740+
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namesfGFP
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)720
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The terminator B0015 from the pBEAST-sfGFP plasmid in the publication was replaced by T500 as the original strain was found to exhibit some recombination events.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pBEAST2-sfGFP was a gift from Jerome Bonnet (Addgene plasmid # 126575 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:126575 ; RRID:Addgene_126575) -
For your References section:
Plug-and-play metabolic transducers expand the chemical detection space of cell-free biosensors. Voyvodic PL, Pandi A, Koch M, Conejero I, Valjent E, Courtet P, Renard E, Faulon JL, Bonnet J. Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 12;10(1):1697. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09722-9. 10.1038/s41467-019-09722-9 PubMed 30979906