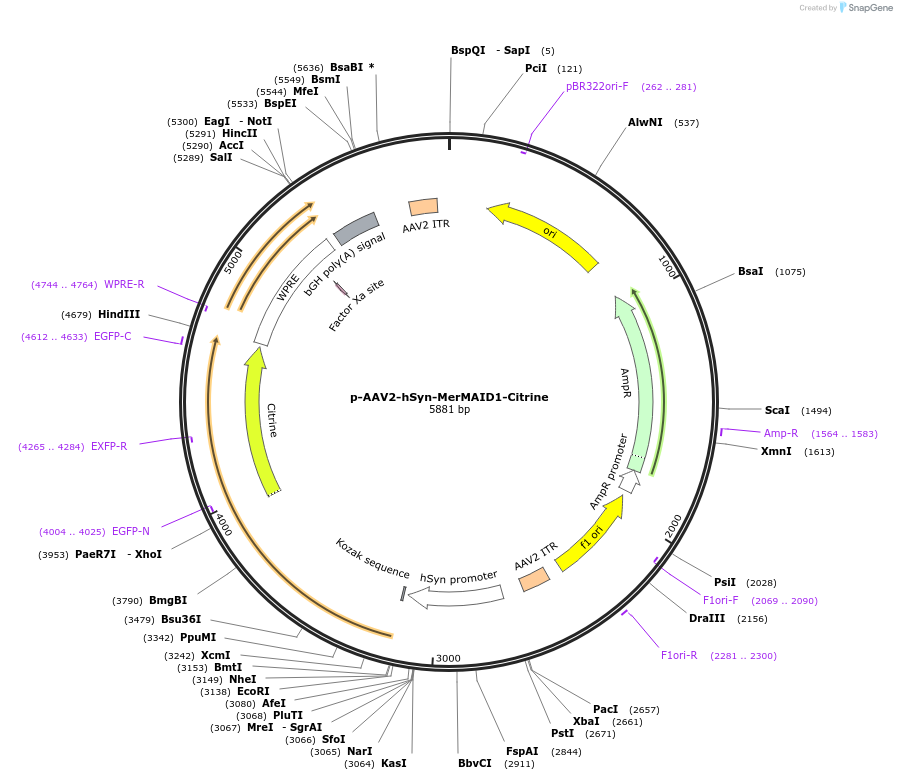
p-AAV2-hSyn-MerMAID1-Citrine
(Plasmid
#126520)
-
PurposeAnion-conducting Channelrhodopsin with near-complete desensitization in continuous light. Codon-optimized for mammalian expression (human/mouse).
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 126520 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepAAV2
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5309
-
Vector typeAAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameMerMAID1
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)786
- Promoter human synapsin
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- Citrine (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer ttcccggccaccttggtcgcgtc
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please visit https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2019/04/12/607804.full.pdf for BioRxiv preprint.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
p-AAV2-hSyn-MerMAID1-Citrine was a gift from Peter Hegemann (Addgene plasmid # 126520 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:126520 ; RRID:Addgene_126520) -
For your References section:
MerMAIDs: a family of metagenomically discovered marine anion-conducting and intensely desensitizing channelrhodopsins. Oppermann J, Fischer P, Silapetere A, Liepe B, Rodriguez-Rozada S, Flores-Uribe J, Peter E, Keidel A, Vierock J, Kaufmann J, Broser M, Luck M, Bartl F, Hildebrandt P, Simon Wiegert J, Beja O, Hegemann P, Wietek J. Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 25;10(1):3315. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11322-6. 10.1038/s41467-019-11322-6 PubMed 31346176