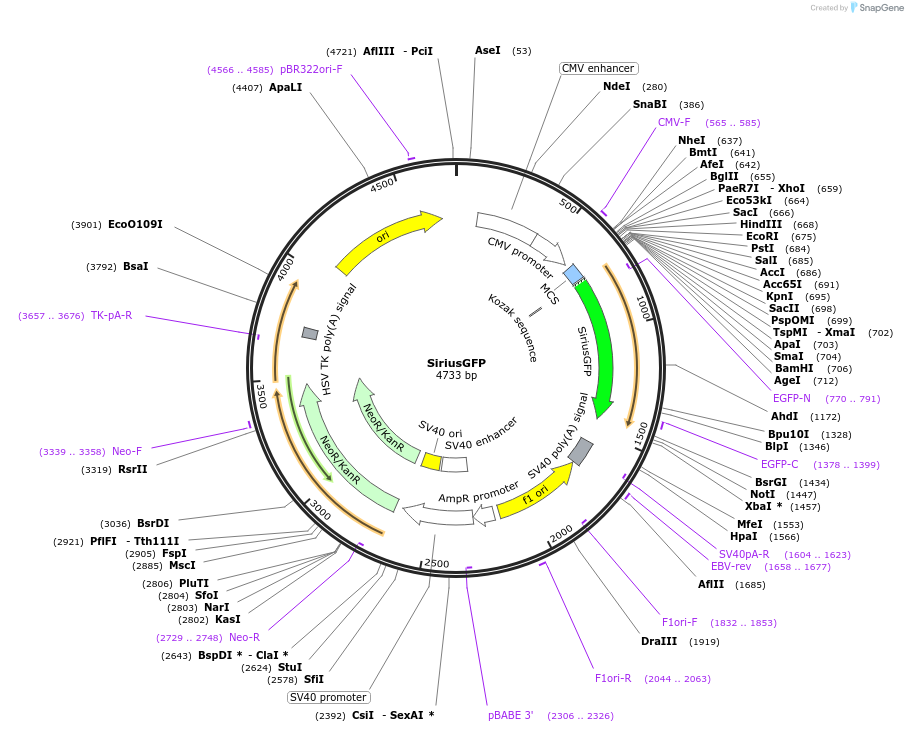
SiriusGFP
(Plasmid
#123201)
-
PurposeWe have developed a variant of eGFP, SiriusGFP, that shows over a two fold increase in photostability with utility in methods requiring sustained or high intensity excitation as in 4D confocal or SIM.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 123201 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepEGFP-N1
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4016
- Total vector size (bp) 4733
-
Modifications to backboneN/A
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Bacterial Expression, Mouse Targeting
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameSiriusGFP
-
Alt nameSiriusGFP-N1
-
Speciesjellyfish
-
Insert Size (bp)717
-
MutationeGFP-S30R/Y39N/F99S/N105T/S147R/M153T/V163A/S205V/A206K
- Promoter CMV
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- N/A
- N/A
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI, BamHI, AgeI, etc. (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI, MfeI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GGTTTAGTGAACCGTCAGATCC
- 3′ sequencing primer TGTTTCAGGTTCAGGG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
SiriusGFP was a gift from Joseph Santos-Sacchi (Addgene plasmid # 123201 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:123201 ; RRID:Addgene_123201) -
For your References section:
Seeing the long tail: A novel green fluorescent protein, SiriusGFP, for ultra long timelapse imaging. Zhong S, Rivera-Molina F, Rivetta A, Toomre D, Santos-Sacchi J, Navaratnam D. J Neurosci Methods. 2019 Feb 1;313:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.12.008. Epub 2018 Dec 19. 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.12.008 PubMed 30578868