-
PurposeFRET biosensor. To monitor histone H3 lysine 9 tri-methylation in mammalian cells by FRET
-
Depositing Lab
-
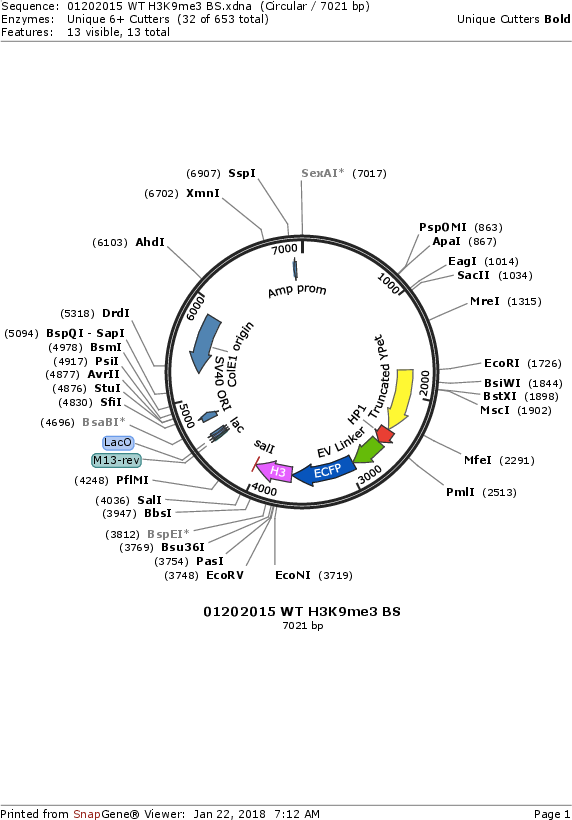
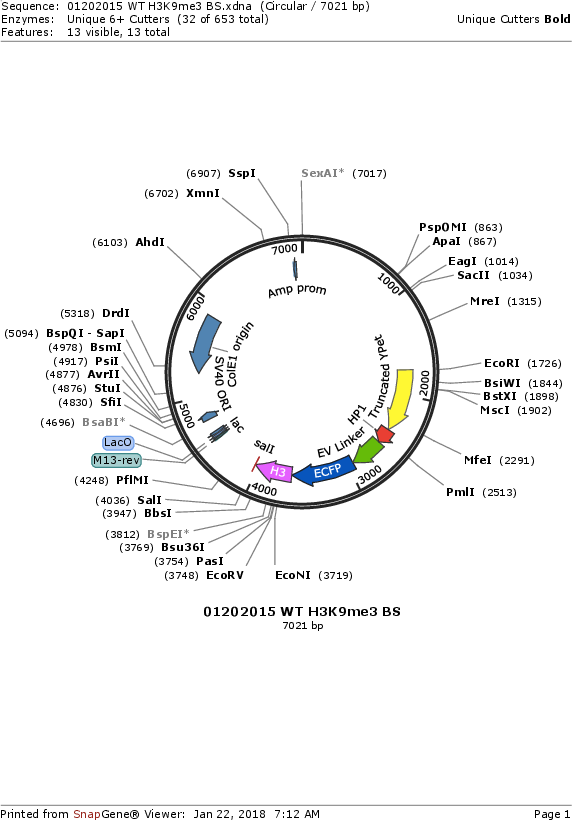
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 120802 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepCAGGS vector
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4717
- Total vector size (bp) 7021
-
Modifications to backboneone BsaI site is mutated
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameTruncated YPet-HP1-EV linker-ECFP-mouse histone H3
-
SpeciesM. musculus (mouse), D. melanogaster (fly), Synthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)2304
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site SalI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GCCTCTGCTAACCATGTTCATGCC
- 3′ sequencing primer CAGATGCTCAAGGGGCTTCATG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
H3K9me3 biosensor was a gift from Yingxiao Wang (Addgene plasmid # 120802 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:120802 ; RRID:Addgene_120802) -
For your References section:
Coordinated histone modifications and chromatin reorganization in a single cell revealed by FRET biosensors. Peng Q, Lu S, Shi Y, Pan Y, Limsakul P, Chernov AV, Qiu J, Chai X, Shi Y, Wang P, Ji Y, Li YJ, Strongin AY, Verkhusha VV, Izpisua Belmonte JC, Ren B, Wang Y, Chien S, Wang Y. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 26. pii: 1811818115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811818115. 10.1073/pnas.1811818115 PubMed 30478057