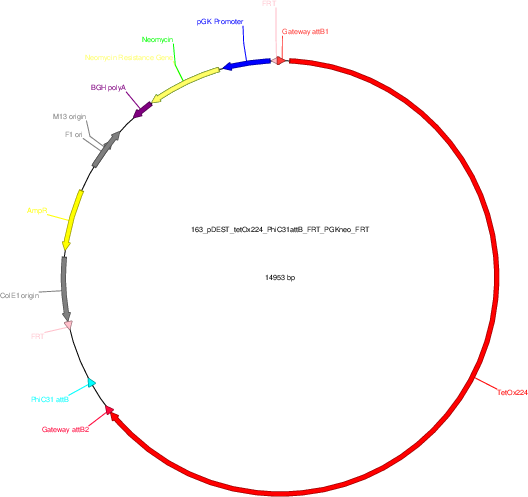
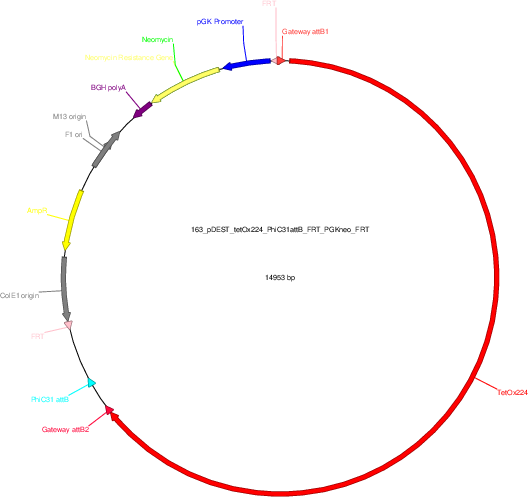
pDEST-tetOx224_PhiC31attB_FRT-PGKneo-FRT
(Plasmid
#119902)
-
PurposePhiC31 integration plasmid for tetO array with Neo selection cassette
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 119902 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepDEST-PhiC31attB-FRT-PGK-neo-FRT
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5464
- Total vector size (bp) 14953
-
Vector typeMouse Targeting
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nametetOx224 array
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)9489
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
PhiC31 integrase expression plasmid available on addGene (pPGKPhiC31obpA: #13795).
The repetitive sequences in this plasmid can be unstable while propagated in bacteria. It is recommended that the repetitive insert be verified by restriction digest and repeat counts be viewed as an approximation.
Please visit https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/409672v1 for bioRxiv preprint.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pDEST-tetOx224_PhiC31attB_FRT-PGKneo-FRT was a gift from Orion Weiner (Addgene plasmid # 119902) -
For your References section:
Live-cell imaging reveals enhancer-dependent Sox2 transcription in the absence of enhancer proximity. Alexander JM, Guan J, Li B, Maliskova L, Song M, Shen Y, Huang B, Lomvardas S, Weiner OD. Elife. 2019 May 24;8. pii: 41769. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41769. 10.7554/eLife.41769 PubMed 31124784