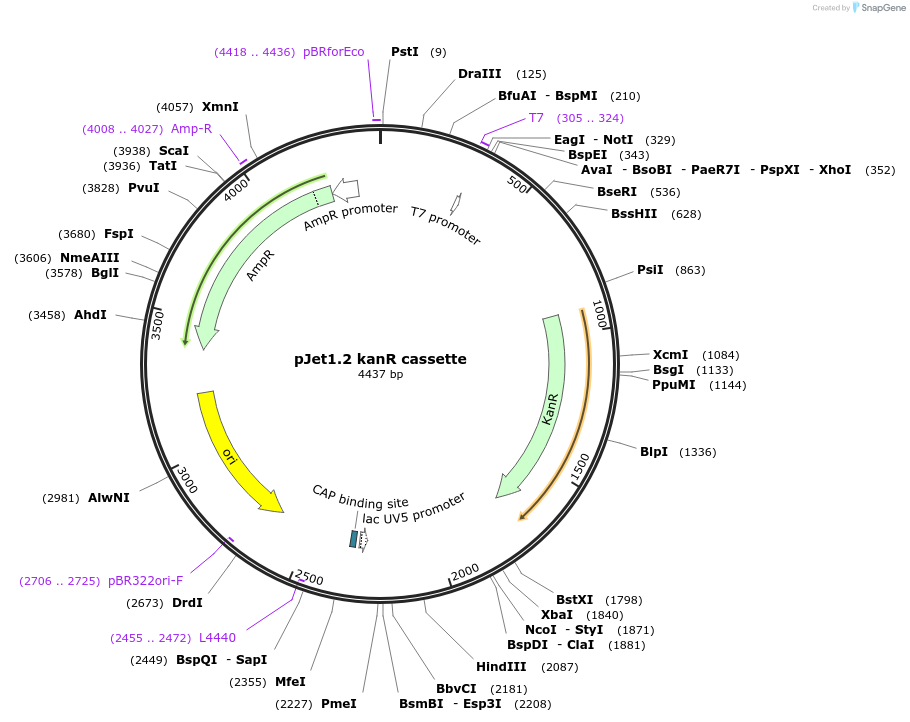
pJet1.2 kanR cassette
(Plasmid
#117122)
-
PurposeKanamycin resistance cassette
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 117122 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepJet1.2
-
Backbone manufacturerThermo scientific
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 2974
- Total vector size (bp) 4440
-
Vector typeGolden gate donor vector for gene targeting in Bacillus subtilis
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameKanamycin resistance cassette for Bacillus subtilis selection
-
SpeciesBacillus subtilis
-
Insert Size (bp)1440
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer CGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGCGGC
- 3′ sequencing primer AAGAACATCGATTTTCCATGGCAG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Donor vector that encodes for a Kanamycin selection marker for Golden gate assembly reactions. Overhangs generated upon BsaI cleavage : AATA (Rup) and TCTA (Rdo).
(Gruber lab reference pSG723)
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pJet1.2 kanR cassette was a gift from Stephan Gruber (Addgene plasmid # 117122 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:117122 ; RRID:Addgene_117122) -
For your References section:
High-Throughput Allelic Replacement Screening in Bacillus subtilis. Diebold-Durand ML, Burmann F, Gruber S. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2004:49-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9520-2_5. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9520-2_5 PubMed 31147909