-
Depositing Lab
-
Publication
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 11182 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
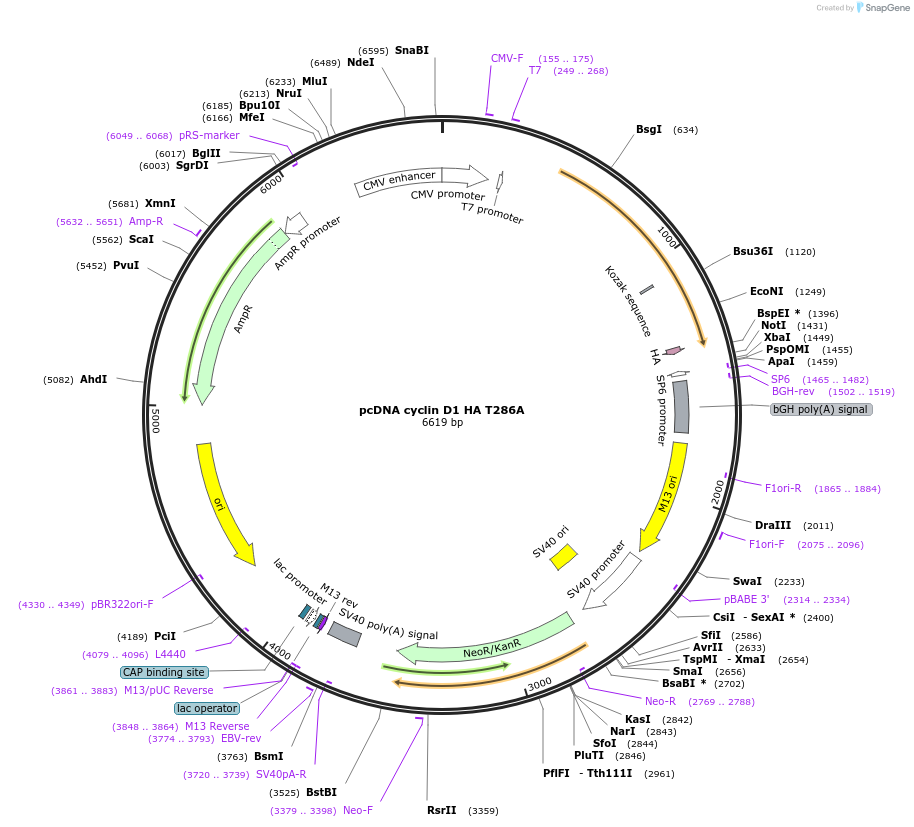
Vector backbonepcDNA3?
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5400
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namecyclin D1 T286A
-
Alt namecyclin D1
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)1120
-
MutationT286A. Mutant that cannot be degraded via the ubiquitin pathway.
-
GenBank IDBC025302
-
Entrez GeneCCND1 (a.k.a. BCL1, D11S287E, PRAD1, U21B31)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- HA (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site XhoI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer T7
- 3′ sequencing primer SP6
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Constructed using site-directed mutagenesis on the parent plasmid, pcDNA cyclinD1 HA, using the primers 5'-acctggcttgcgcacccaccgacg-3' and 5'-cgtcggtgggtgcgcaagccaggt-3'.
Note: The author's map and author's sequence are not fully correct. EcoRI and XhoI are not unique sites in this plasmid.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pcDNA cyclin D1 HA T286A was a gift from Bruce Zetter (Addgene plasmid # 11182 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:11182 ; RRID:Addgene_11182) -
For your References section:
Antizyme targets cyclin D1 for degradation. A novel mechanism for cell growth repression. Newman RM, Mobascher A, Mangold U, Koike C, Diah S, Schmidt M, Finley D, Zetter BR. J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 1. 279(40):41504-11. 10.1074/jbc.M407349200 PubMed 15277517