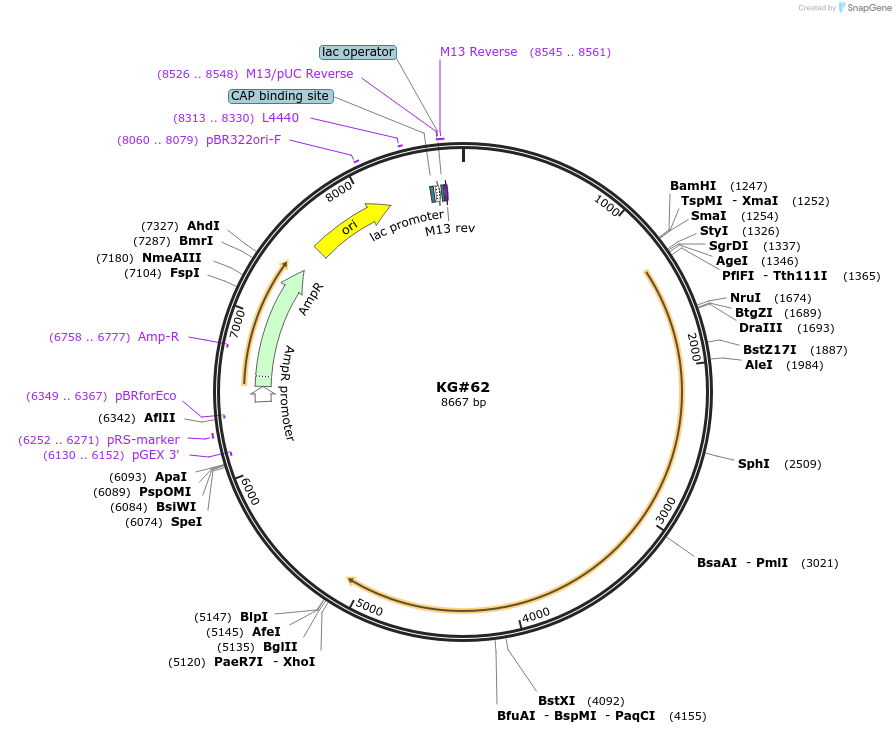
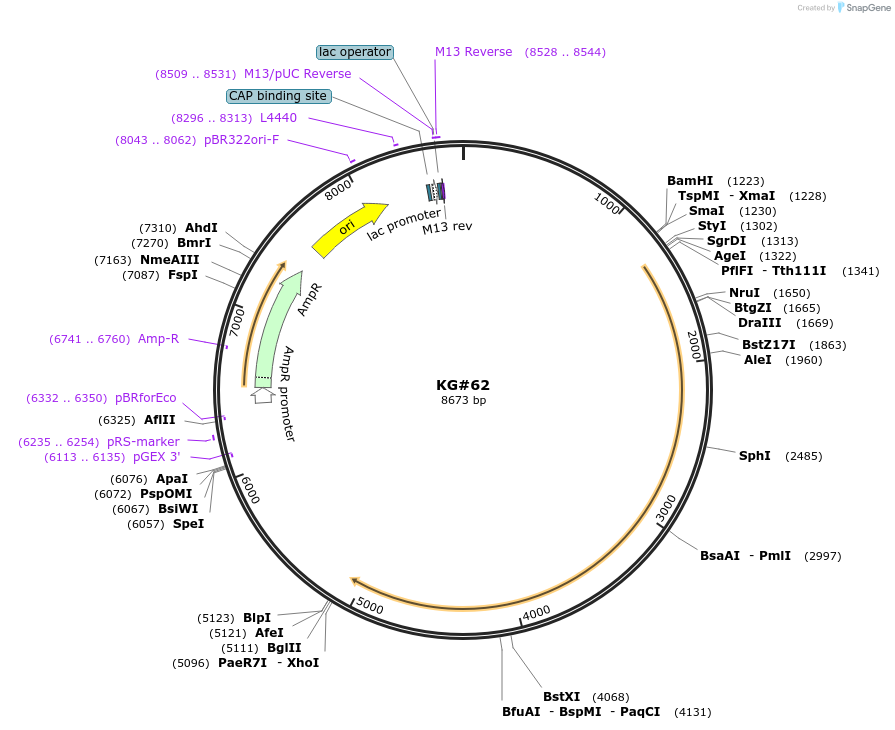
KG#62
(Plasmid
#110874)
-
PurposeExpresses the C. elegans acy-1 cDNA pan-neuronally
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 110874 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepUC
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 2617
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Growth instructionsAlways streak out this culture for single colonies and do minipreps on >= 4 clones (~1/2 of colonies will be right). Choose small colonies after 18 - 20h growth. DNA yeild is low (~170 ng/ ul x 30 ul for a Qiagen 3 ml miniprep).
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert namerab-3 promoter
-
SpeciesC. elegans (nematode)
-
Insert Size (bp)1208
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 1
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer Unknown
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert nameacy-1 cDNA
-
SpeciesC. elegans (nematode)
-
Insert Size (bp)3762
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 2
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer Unknown
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 3
-
Gene/Insert nameunc-54 3' control region with 1 intron just upstream and 1 intron in control region
-
SpeciesC. elegans (nematode)
-
Insert Size (bp)978
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 3
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer Unknown
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Always streak out this culture for single colonies and do minipreps on >= 4 clones (~1/2 of colonies will be right). Choose small colonies after 18 - 20h growth. DNA yeild is low (~170 ng/ ul x 30 ul for a Qiagen 3 ml miniprep).
Used Pfu Ultra polymerase and primers engineered with restriction sites to amplify the 3.8 Kb acy-1 cDNA coding region from KG#61 and cloned into Age I/ Xho I cut KG#59 (rab-3:: expression vector). Transform into XL1-Blue electrocompetent cells. Miniprepped 8 clones to find those with correct size insert and vector, then submitted 2 clones for sequence. Chose one clone that has correct sequence and made glycerol stock.
Features of the expression construct: This expression construct has a promoter (rab-3) that will drive strong and specific expression of acy-1 cDNA in the entire nervous system of juvenile and adult animals. Other features of the expression vector include a "decoy" 5' to the promoter to reduce non-specific expression in the gut (see Fire Lab 1995 Kit documentation for description), the unc-54 3' end including the poly A addition signal, and 3 introns (1 in 5' UTR, 1 just upstream of the unc-54 3' end, and 1 inserted in the unc-54 3' end). These introns help provide more uniform and robust expression, especially if you are expressing a cDNA with no introns (as we are) as opposed to a gene with introns. The sequence AAAA is engineered just after the 5' restriction site and just before the initiator ATG to provide a consensus translation start site. The sequence AT follows the stop codon and immediately precedes the 3' restriction site to provide a consensus post - stop codon sequence. The vector provides the unc-54 3' UTR and control region. Note: the acy-1 cDNA from which this clone was produced corresponds to the single acy-1 cDNA predicted by wormbase, which is F17C8.1
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
KG#62 was a gift from Kenneth Miller (Addgene plasmid # 110874 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:110874 ; RRID:Addgene_110874) -
For your References section:
Convergent, RIC-8-dependent Galpha signaling pathways in the Caenorhabditis elegans synaptic signaling network. Reynolds NK, Schade MA, Miller KG. Genetics. 2005 Feb;169(2):651-70. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.031286. Epub 2004 Oct 16. 10.1534/genetics.104.031286 PubMed 15489511