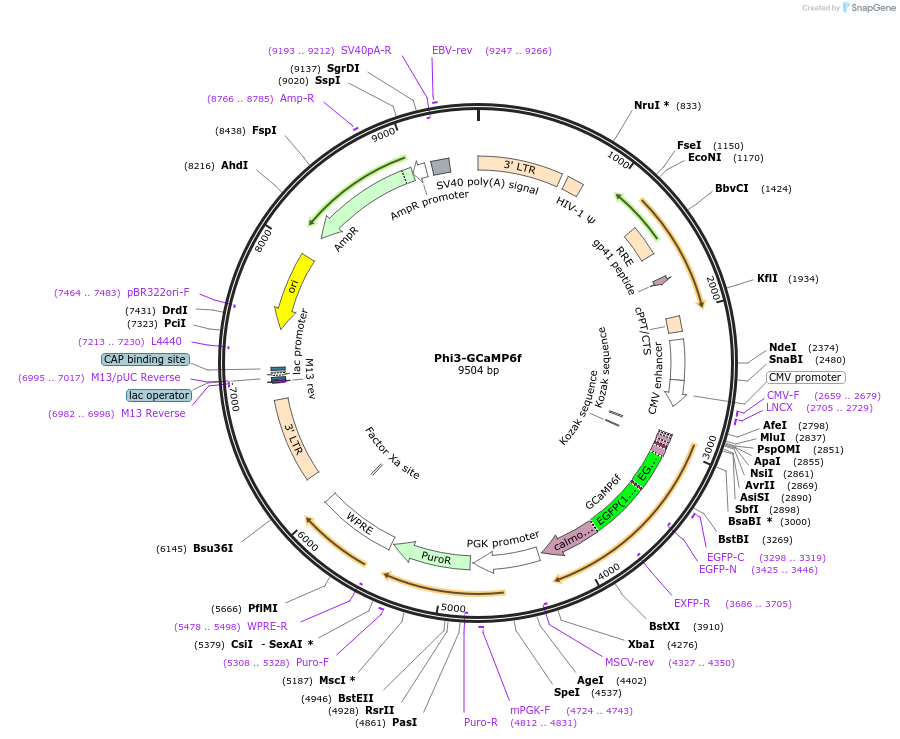
Phi3-GCaMP6f
(Plasmid
#106298)
-
PurposeCMV driven GFP based calcium (Ca2+) reporter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 106298 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonePLVX Puro
-
Backbone manufacturerClontech
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 8151
- Total vector size (bp) 9504
-
Modifications to backboneMCS was modified as described in Takacs, C.N., et al., (2017) Traffic 18, 192-204.
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Lentiviral
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameGCaMP6f
-
Alt nameGCaMP3-T302L R303P A317E D380Y T381R S383T R392G
-
Alt nameGCaMP3 variant 693
-
SpeciesR. norvegicus (rat), G. gallus (chicken); A. victoria (jellyfish)
-
Insert Size (bp)1353
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BglII (GCaMP6f) and BamHI (Phi3) (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site XbaI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG
- 3′ sequencing primer GCGCATGCTCCAGACTGCC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byGCaMP6f was from Douglas Kim, Addgene plasmid # 40755
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
Phi3-GCaMP6f was a gift from Sanford Simon (Addgene plasmid # 106298 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:106298 ; RRID:Addgene_106298) -
For your References section:
Ca2+ transients in melanocyte dendrites and dendritic spine-like structures evoked by cell-to-cell signaling. Belote RL, Simon SM. J Cell Biol. 2020 Jan 6;219(1). pii: 132739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201902014. 10.1083/jcb.201902014 PubMed 31821412