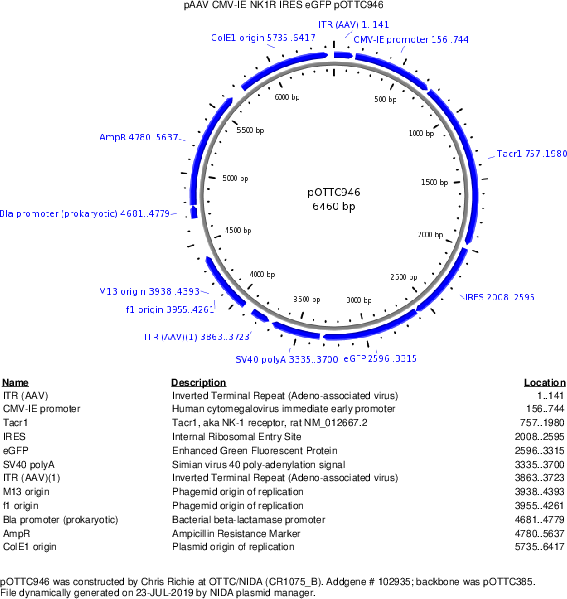
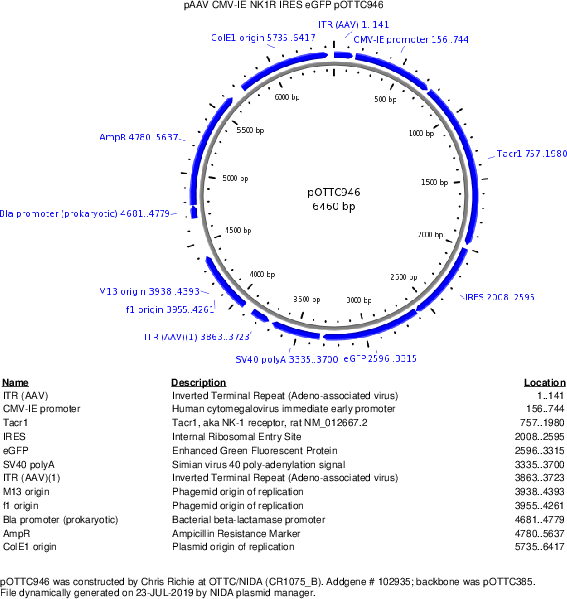
pOTTC946 - pAAV CMV-IE NK1R-IRES-EGFP
(Plasmid
#102935)
-
PurposeAn AAV vector that expresses rat NK1R-IRES-EGFP under the CMV-IE promoter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 102935 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |

Want a viral vector made from this plasmid?
Make a packaging request and we'll get back to you.
Please log in to submit a packaging request.
-
SerotypeSelect serotype for details See details about
-
PricingSelect serotype and quantity $ USD for preparation of µL virus + $30 USD for plasmid.
-
How this works
- Place a request for a quantity of 10 (1 mL), 25 (2.5 mL), or 50 (5 mL). Our all-inclusive pricing includes DNA production and QC.
- Addgene will quickly confirm that we can produce a high-quality prep for you.
- Track your request and place an order from within your account. Payment information must be added before we can begin processing your order.
- Receive your prep in 6–9 weeks after the MTA is approved by your organization.
- Learn more about our Packaged on Request Service.
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepOTTC385
-
Backbone manufacturerChris Richie
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5236
- Total vector size (bp) 6460
-
Modifications to backboneNA
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature30°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameNK1R
-
Alt nameTACR1
-
SpeciesR. norvegicus (rat)
-
Insert Size (bp)1224
-
GenBank IDNM_012667.2
-
Entrez GeneTacr1 (a.k.a. Tac1r)
- Promoter CMV-IE
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV F: CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG
- 3′ sequencing primer SV40pA R: TTCAGGTTCAGGGGGAGGTG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pOTTC946 - pAAV CMV-IE NK1R-IRES-EGFP was a gift from Brandon Harvey (Addgene plasmid # 102935 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:102935 ; RRID:Addgene_102935) -
For your References section:
Escalated Alcohol Self-Administration and Sensitivity to Yohimbine-Induced Reinstatement in Alcohol Preferring Rats: Potential Role of Neurokinin-1 Receptors in the Amygdala. Nelson BS, Fulenwider HD, Nennig SE, Smith BM, Sequeira MK, Chimberoff SH, Richie CT, Cheng K, Rice KC, Harvey BK, Heilig M, Schank JR. Neuroscience. 2019 Jun 23;413:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.06.023. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.06.023 PubMed 31242442