CRISPR Plasmids: Nick
Cas nickase mutants introduce gRNA-targeted single-strand breaks in DNA instead of the double-strand breaks created by wild-type Cas enzymes. To use a nickase mutant, you will need two gRNAs that target opposite strands of your DNA in close proximity. These double nicks create a double-strand break (DSB) that is repaired using error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Double nicking strategies reduce unwanted off-target effects. Nickase mutants can also be used with a repair template to introduce specific edits via homology-directed repair (HDR).
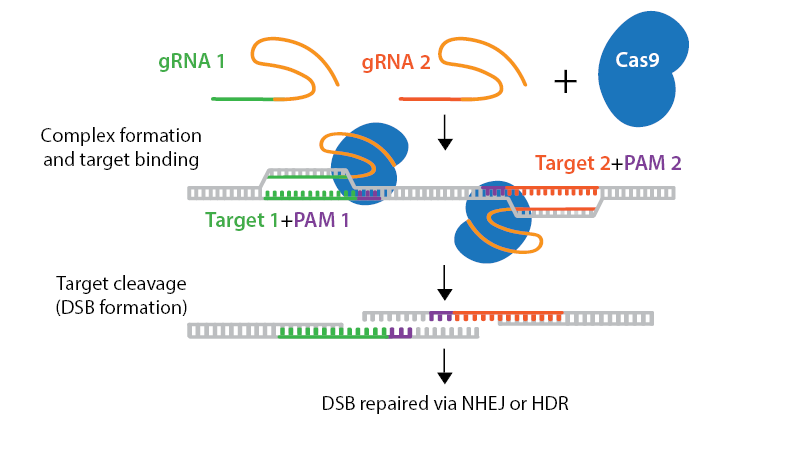
Browse, sort, or search the tables below for CRISPR nickase plasmids. To learn more about CRISPR nickases and other CRISPR topics, read our CRISPR Guide.
Mammalian
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Bacteria
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Drosophila
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Plant
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Yeast
| ID | Plasmid | Description | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
CRISPR Resources
Addgene has a large selection of CRISPR plasmids and resources. Find more CRISPR functions along with plasmids categorized by organism by visiting our CRISPR plasmids page. Find a comprehensive list of CRISPR resources by visiting our CRISPR reference page.
Content last reviewed: 17 October 2025
Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!



